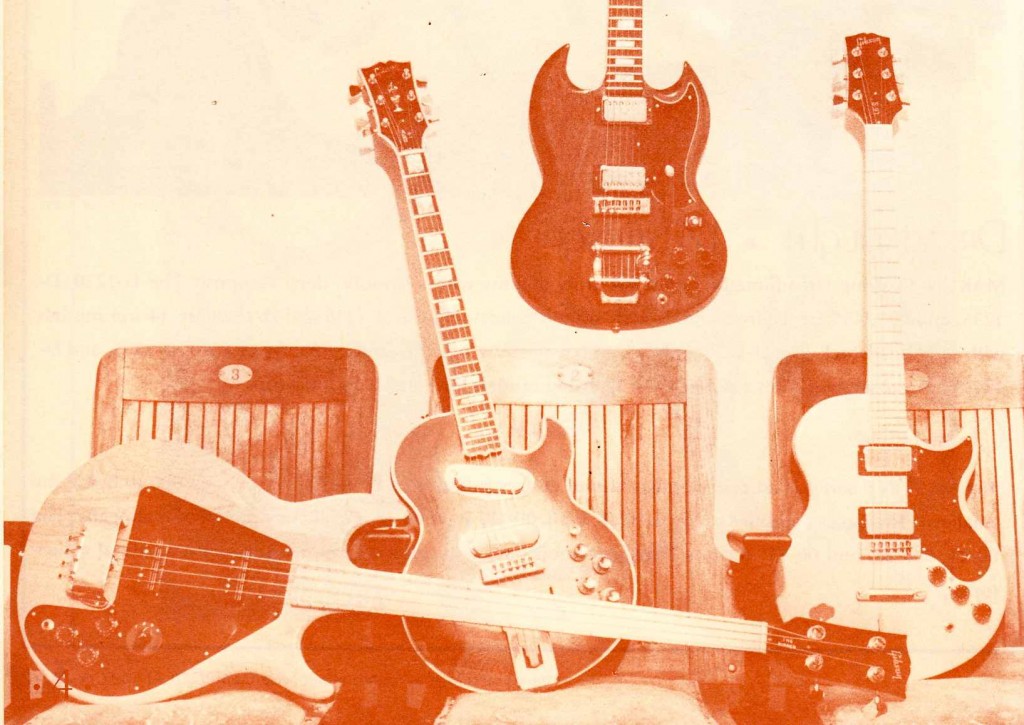
Download a twenty-three-page excerpt of the 1975 catalog from Music Emporium of Bethesda, Maryland (h.f. ‘ME’):
Download a twenty-three-page excerpt of the 1975 catalog from Music Emporium of Bethesda, Maryland (h.f. ‘ME’):
DOWNLOAD: Music_Emporium_1975_Catalog
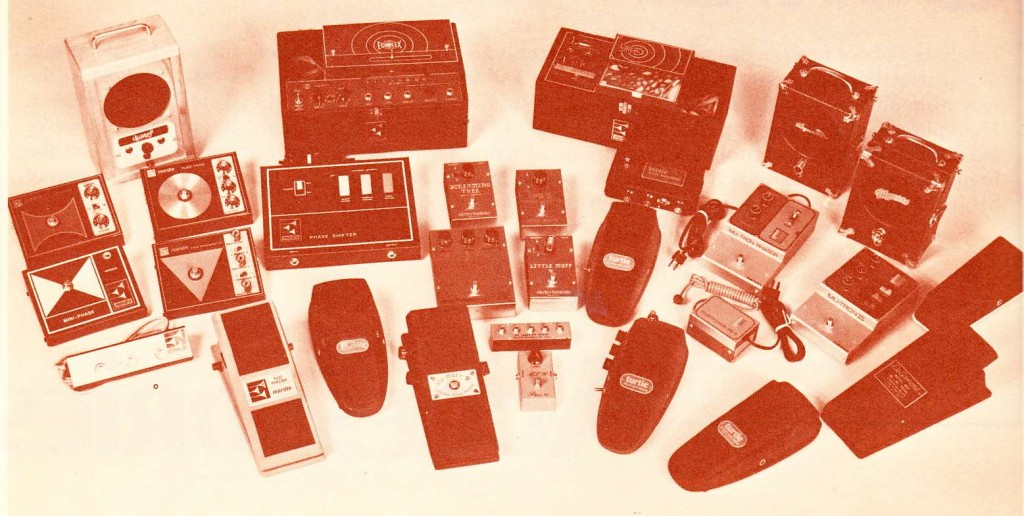
Products covered, with vague text, no specs (or prices), and moody photography/impressionistic illustration, include: 1975 Martin D-18, D-28, D-35, etc; Gibson Les Paul bass, Triumph, Signature, ES-335TD-SV, ES-345TD, among others; Gibson J-200, Blue Ridge 12, and J-55; Dobro 60D, 33, 90, and 35 resonator guitars; Guild F-50, F-40, D-50, F-212XL, among others; Fender Telecaster, Telecaster Deluxe, Thinline, Precision, Jazz, and Telecaster Basses; the Bradley line of directly-imported MIJ ‘Lawsuit’ guitars, including the Doubleneck, FV-60, ES-775, TE350, JB60-W, ST50-N, LP65-N, and LP54; Amplifiers and PA from Acoustic, Ampeg, DB Sound (look similar to Heil, which is also represented), Gollehon PA from Grand Rapids, MI, including their 8218/M, 8218/A, MR-90 Horn, 8220/M and /A models; AKG, Shure, and Maruni Mics; ARP and Moog synthesizers; and a pile of guitar effects pedals that no one can afford anymore.
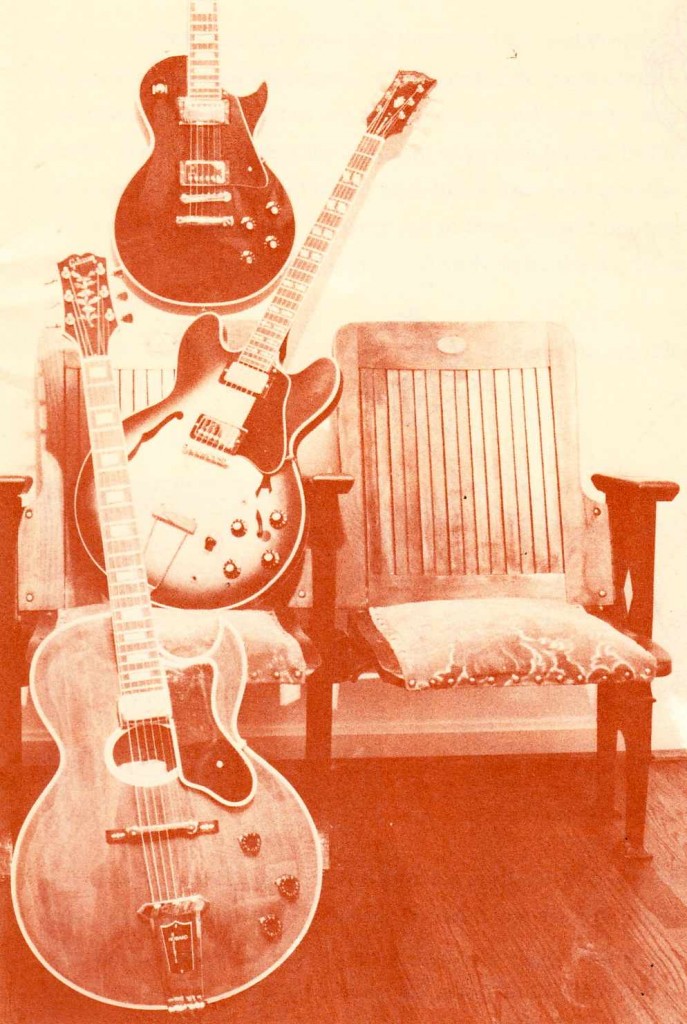
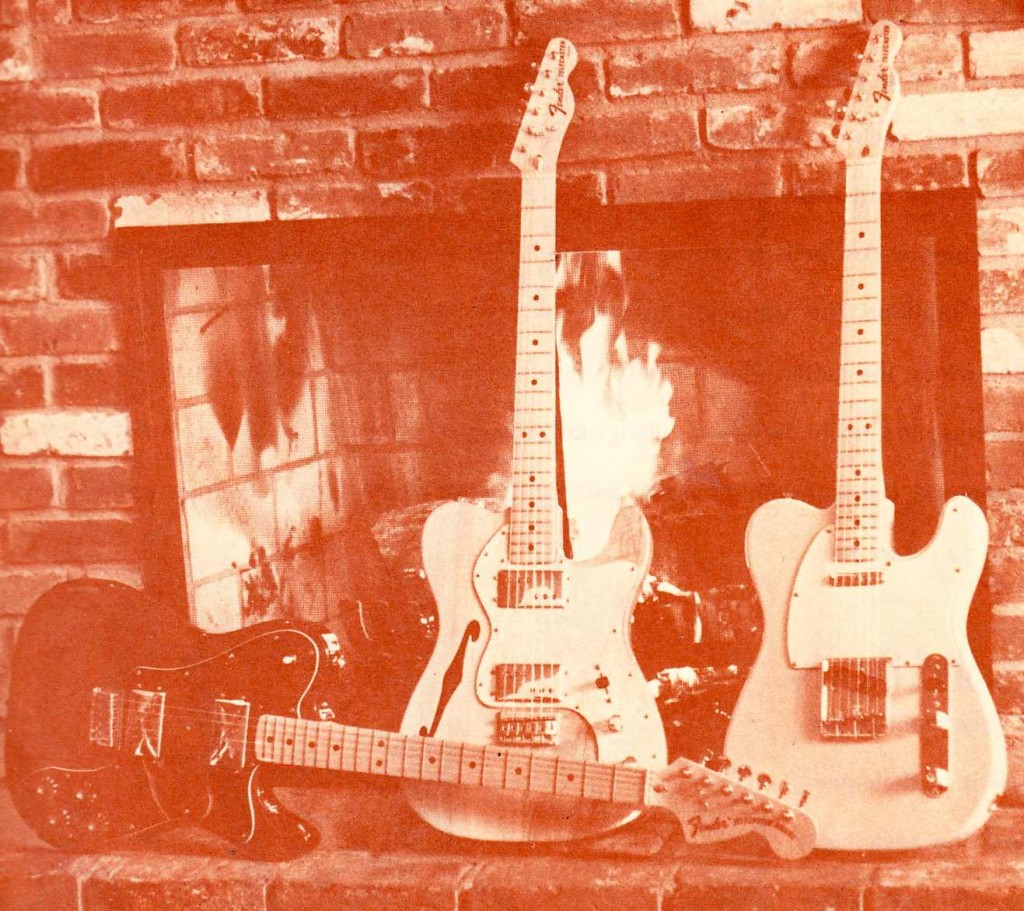

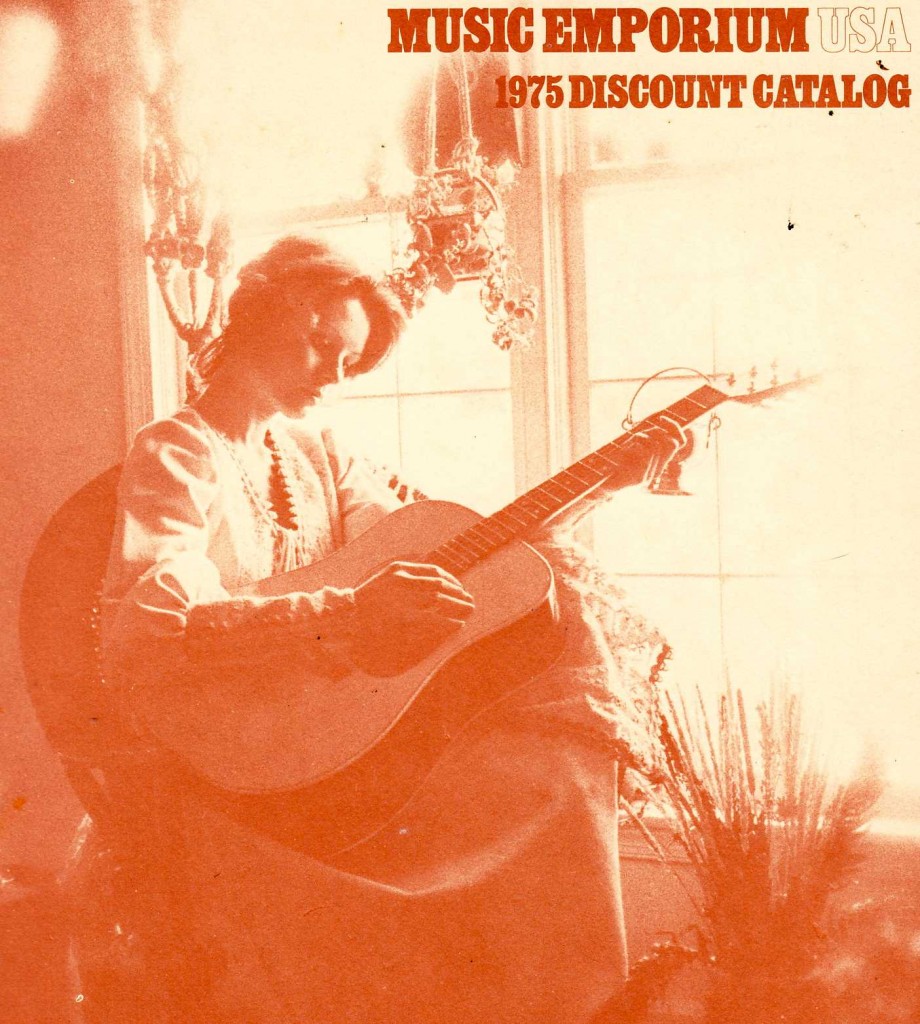
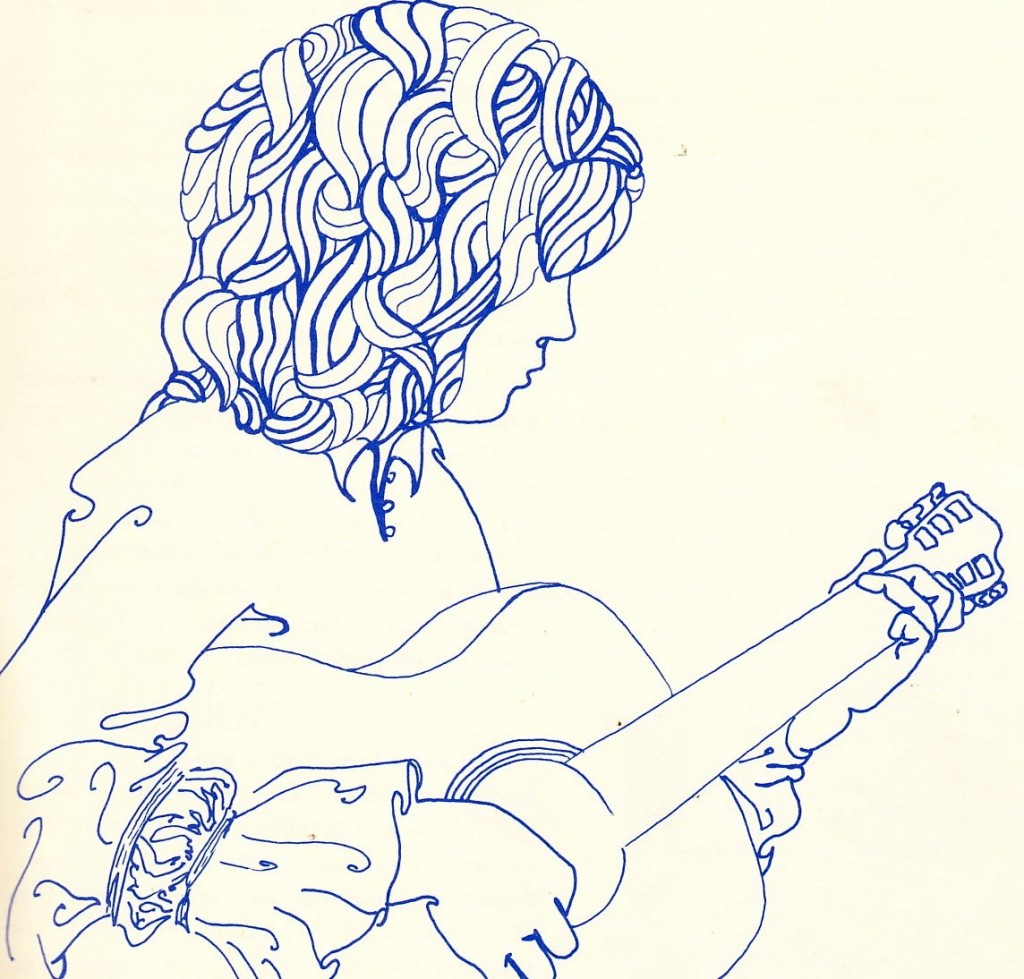
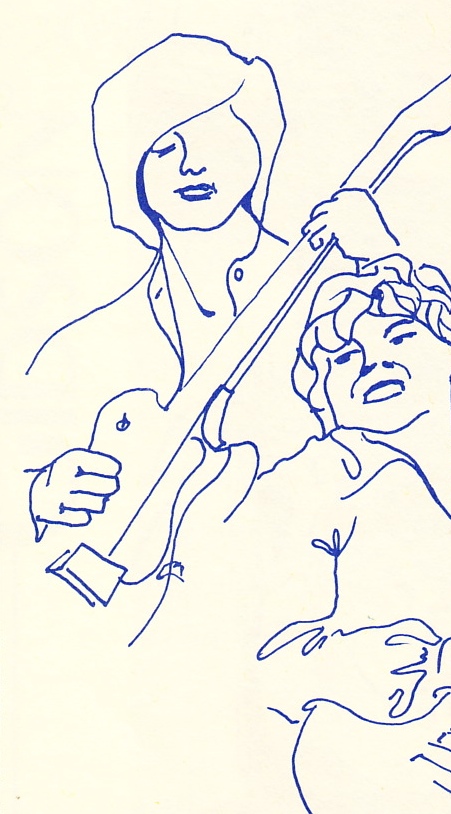
 ME was the catalog division of the family-owned Veneman instrument retail-store business. Veneman was purchased by Guitar Center in 2004. Check out these sepia-tinted photos for a second. Veneman could easily have opted to re-print the images that manufacturers supply through their distributors, but they really went the extra mile; the mood of these images, combined with the glaring lack of any sort of pricing or specifications, seems impossible today as a sales strategy for guitars: ME was selling you an attitude and a vibe first; the particular instruments were secondary. Consider another interesting fact about the images in the catalog: apart from the High Priestess on the cover, there are no almost no photographic image of people in the catalog. Instead we get some beautiful line-illustration work. While this could have been a talent compensation/rights issue, I feel like it’s more of a deliberate move that allows the musician/customer to more easily insert themselves into these instrument-scenarios. I mean, who wants to buy a Les Paul that you see slung around the neck of some bro in a (insert yr least favorite sartorial signifier) shirt?
ME was the catalog division of the family-owned Veneman instrument retail-store business. Veneman was purchased by Guitar Center in 2004. Check out these sepia-tinted photos for a second. Veneman could easily have opted to re-print the images that manufacturers supply through their distributors, but they really went the extra mile; the mood of these images, combined with the glaring lack of any sort of pricing or specifications, seems impossible today as a sales strategy for guitars: ME was selling you an attitude and a vibe first; the particular instruments were secondary. Consider another interesting fact about the images in the catalog: apart from the High Priestess on the cover, there are no almost no photographic image of people in the catalog. Instead we get some beautiful line-illustration work. While this could have been a talent compensation/rights issue, I feel like it’s more of a deliberate move that allows the musician/customer to more easily insert themselves into these instrument-scenarios. I mean, who wants to buy a Les Paul that you see slung around the neck of some bro in a (insert yr least favorite sartorial signifier) shirt?
A possible overall explanation? It’s the Whole Earth Catalog Effect. If yr not familiar with the Whole Earth Catalog (h.f. WEC), and you have any interest whatsoever in American culture of the 1970s, get a copy of an early edition and check it out. It is one of the most seminal documents of the era, as well as being an early precursor of the peer-to-peer information exchange style that we now experience in the form of….yup… the internet. There were about a billion (or googleplex…) copies printed and you can find if for a few bucks at most community book sales or used book shops. Anyhow, WEC was such a powerful and ubiquitous presence among the more liberal and artistic elements of American Society in the 70s that we start to see its editorial and visual style reflected in actual catalogs of the era that were directed at a similar demographic. For another example of this phenomenon, check this…
**************
*******
***
The only really interesting bit as far as the equipment offered is the BRADLEY line of guitars. Bradley was apparently the house-brand of directly-imported Japanese-made guitars which ME exclusively sold.
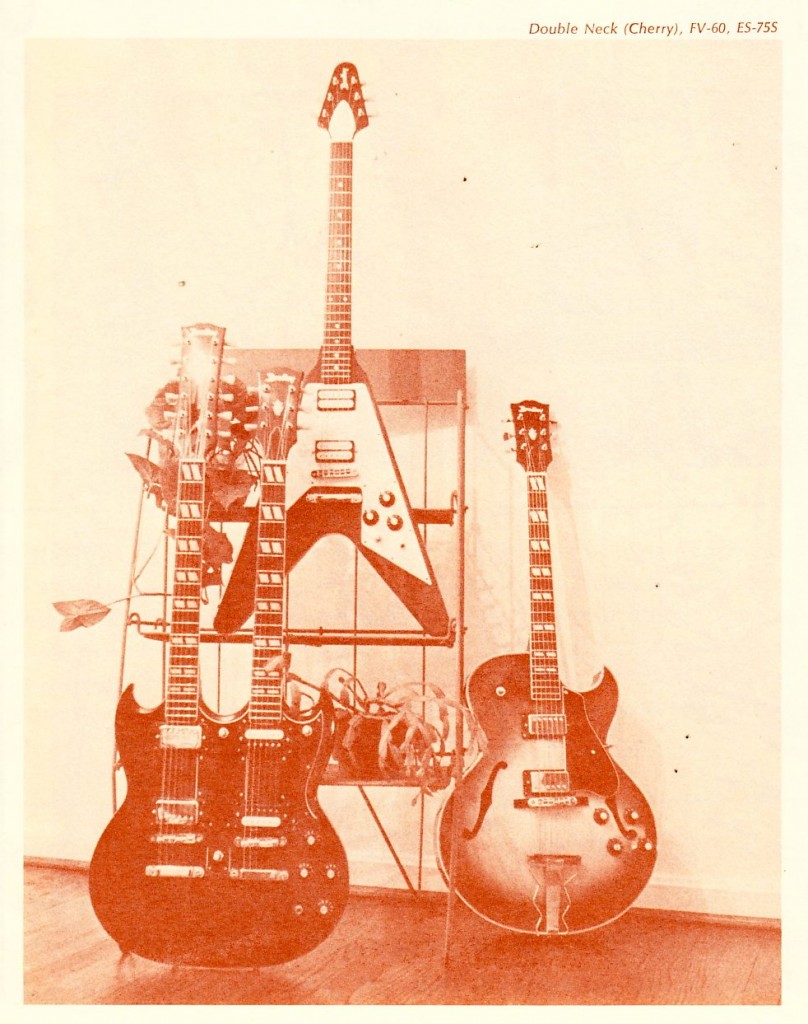
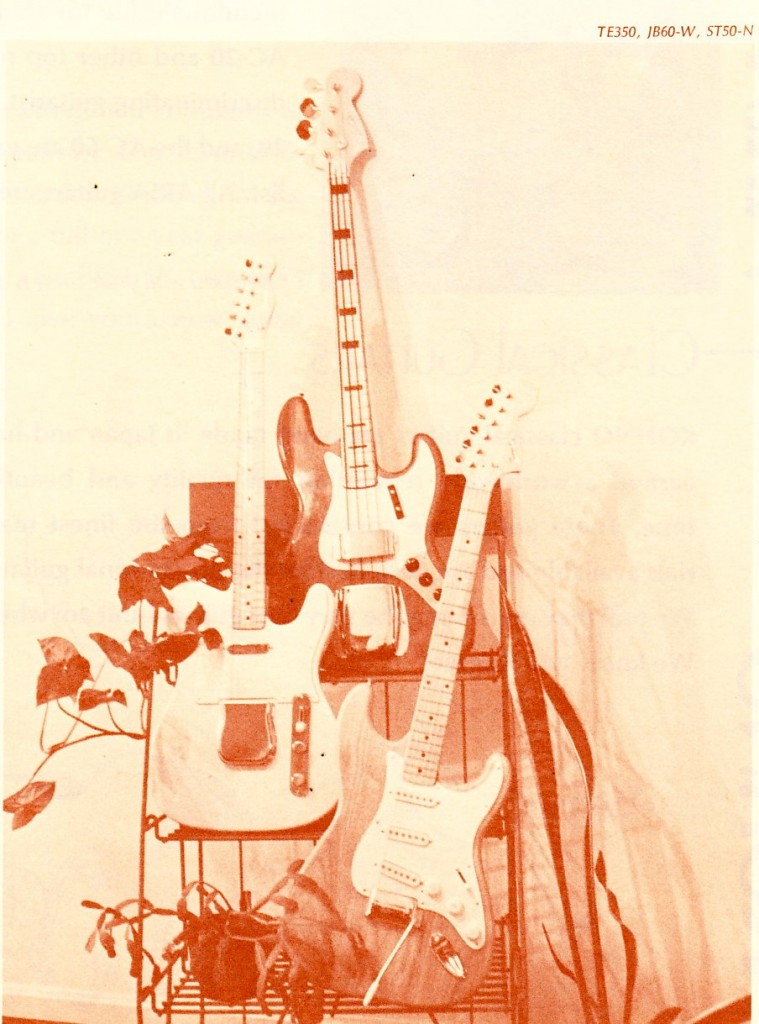
 These sure look like Ibanez to me. Anyone own a 70’s Bradley? Tell us your thoughts. Read some discussion online here.
These sure look like Ibanez to me. Anyone own a 70’s Bradley? Tell us your thoughts. Read some discussion online here.