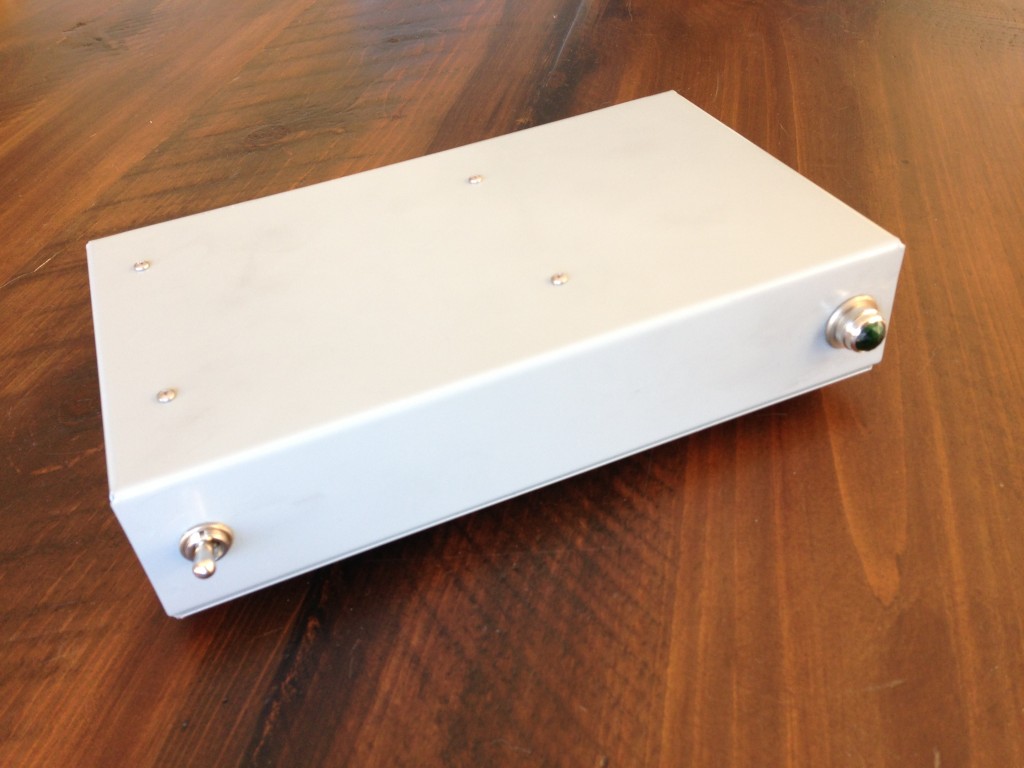
I know. The grey box above ain’t much to look at in the abstract. But, it’s what’s inside the box that we are concerned with today. Jsn at Boozhound Labs (hf ‘BHL’) sent me one of his new “JFEt Phono Preamp Kits” to check out, and I’m glad I did. It was a quick+ easy project that has greatly improved my LP listening situation in the living room mini-system.
I know. The grey box above ain’t much to look at in the abstract. But, it’s what’s inside the box that we are concerned with today. Jsn at Boozhound Labs (hf ‘BHL’) sent me one of his new “JFEt Phono Preamp Kits” to check out, and I’m glad I did. It was a quick+ easy project that has greatly improved my LP listening situation in the living room mini-system.
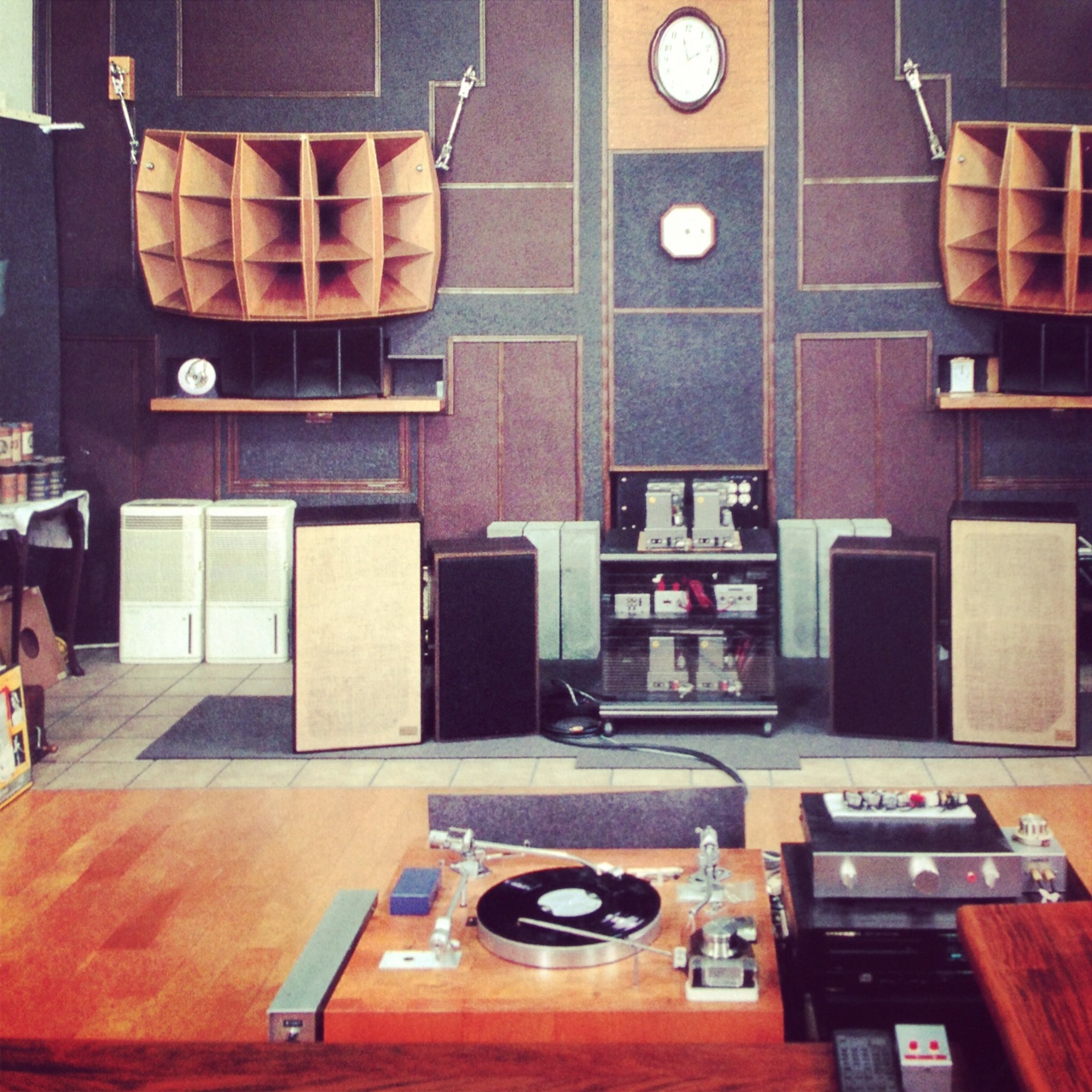
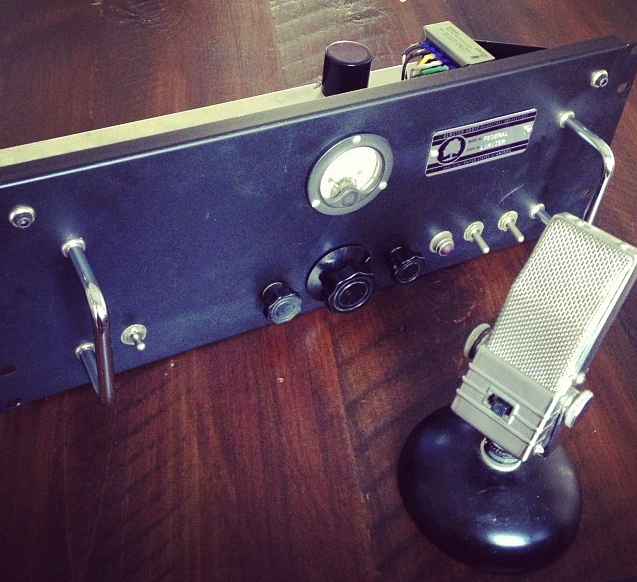
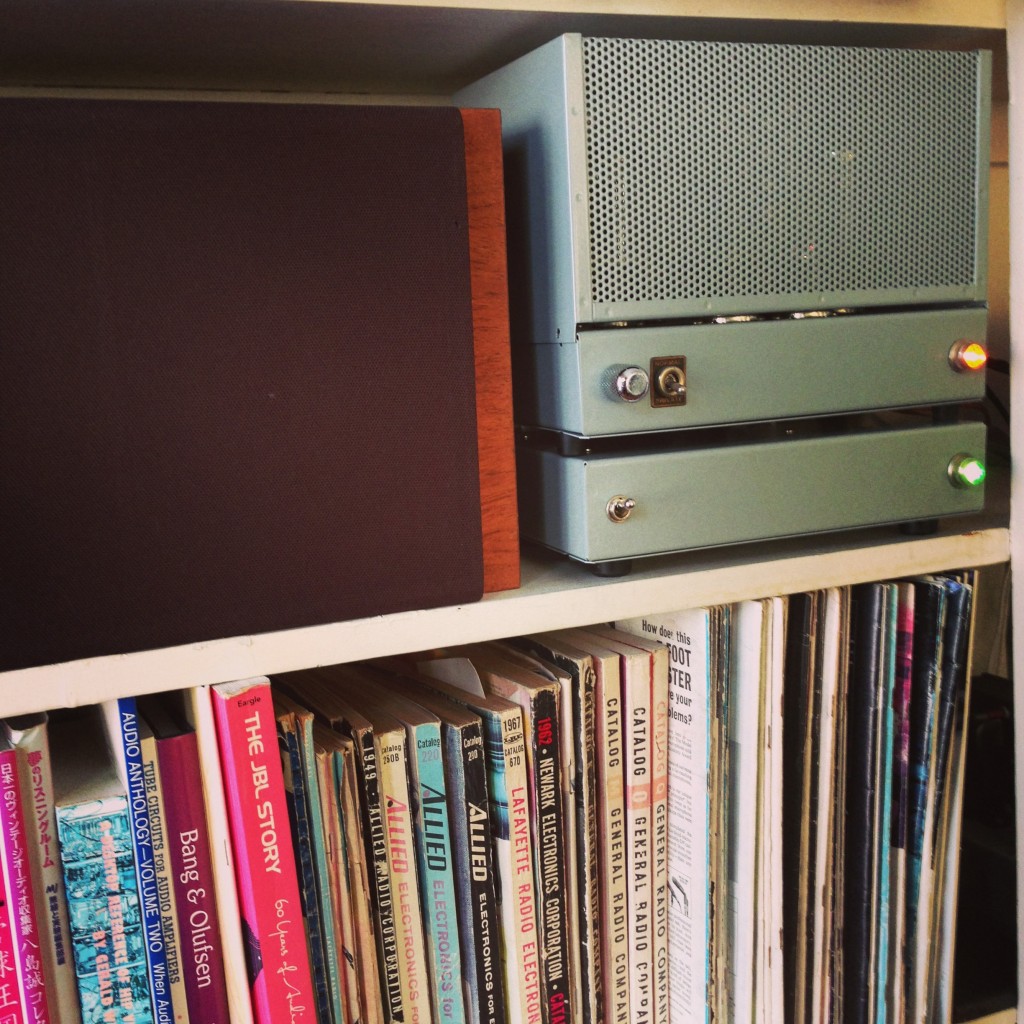 Above you can see the BHL preamp right beneath a little stereo power amp (with A/B input select and a stereo volume pot). The power amp is a design that I have built dozens of times for clients: a single 6SN7 is shared to provide one voltage-gain stage per channel, with each channel using a 6L6 (cathode biased) class-A to provide approx. 8 watts of power to each speaker. Just so you know where I’m coming from, here’s the complete setup: ADC QLM 30 mk III cartridge mounted on a Technics 1200 table, then into the BHL, then to the SE 8-watt power amp, and finally to JBL 18ti speakers. Very circa-1980. The other input of the power amp is connect to an Apple Airport Express so that I can stream music off the iPhone or the macbook. Certainly not an audiophile setup, but I’ve never found it lacking.
Above you can see the BHL preamp right beneath a little stereo power amp (with A/B input select and a stereo volume pot). The power amp is a design that I have built dozens of times for clients: a single 6SN7 is shared to provide one voltage-gain stage per channel, with each channel using a 6L6 (cathode biased) class-A to provide approx. 8 watts of power to each speaker. Just so you know where I’m coming from, here’s the complete setup: ADC QLM 30 mk III cartridge mounted on a Technics 1200 table, then into the BHL, then to the SE 8-watt power amp, and finally to JBL 18ti speakers. Very circa-1980. The other input of the power amp is connect to an Apple Airport Express so that I can stream music off the iPhone or the macbook. Certainly not an audiophile setup, but I’ve never found it lacking.
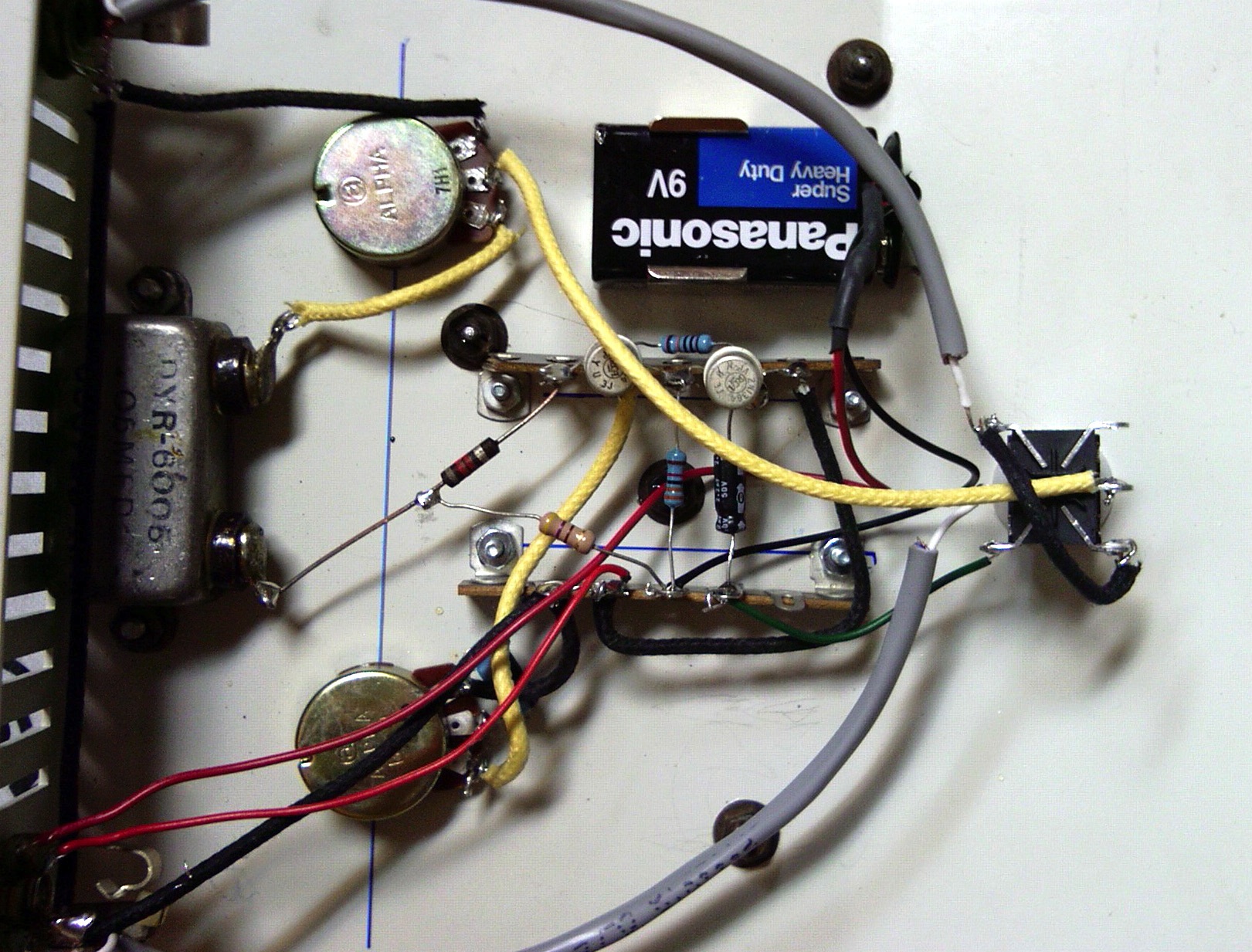
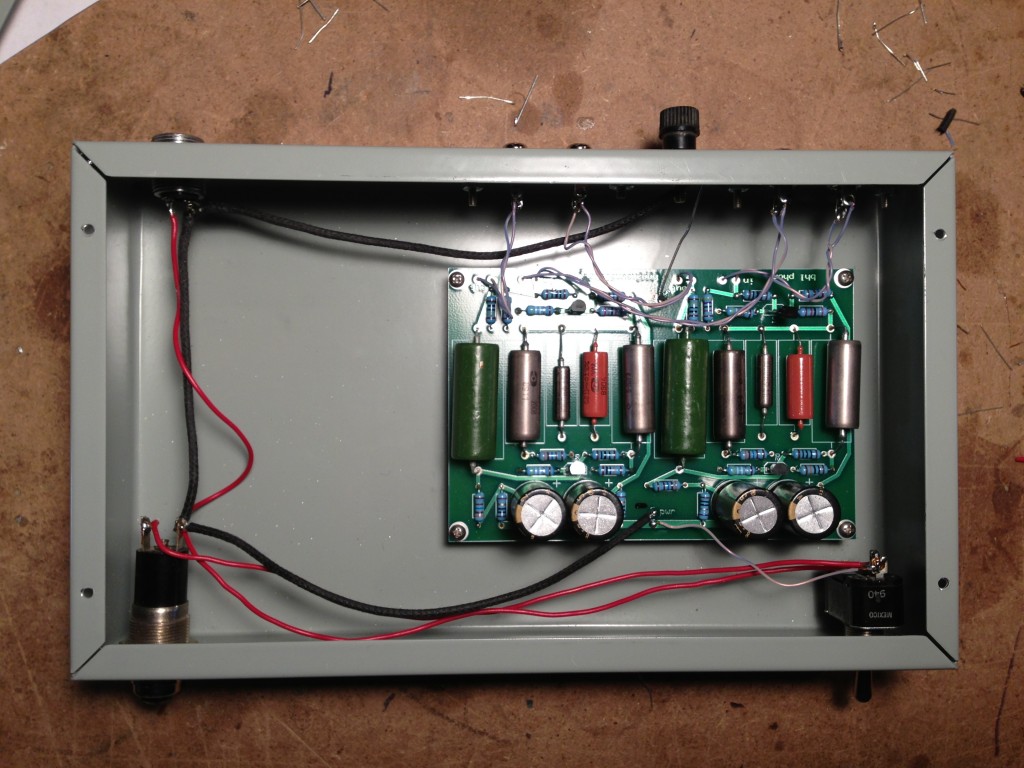 The BHL kit ($89 direct) comprises the board that you see above, all the parts to stuff the board, instructions, and a bunch of good quality wire. I supplied the Hammond steel chassis and bottom plate and the vintage-style lamp holder and big power switch, plus a $13 24v switching power supply from eBay, some El Cheapo-brand dual RCA jacks, a binding post, and a goofy old Amphenol connector to mate the power supply.
The BHL kit ($89 direct) comprises the board that you see above, all the parts to stuff the board, instructions, and a bunch of good quality wire. I supplied the Hammond steel chassis and bottom plate and the vintage-style lamp holder and big power switch, plus a $13 24v switching power supply from eBay, some El Cheapo-brand dual RCA jacks, a binding post, and a goofy old Amphenol connector to mate the power supply.
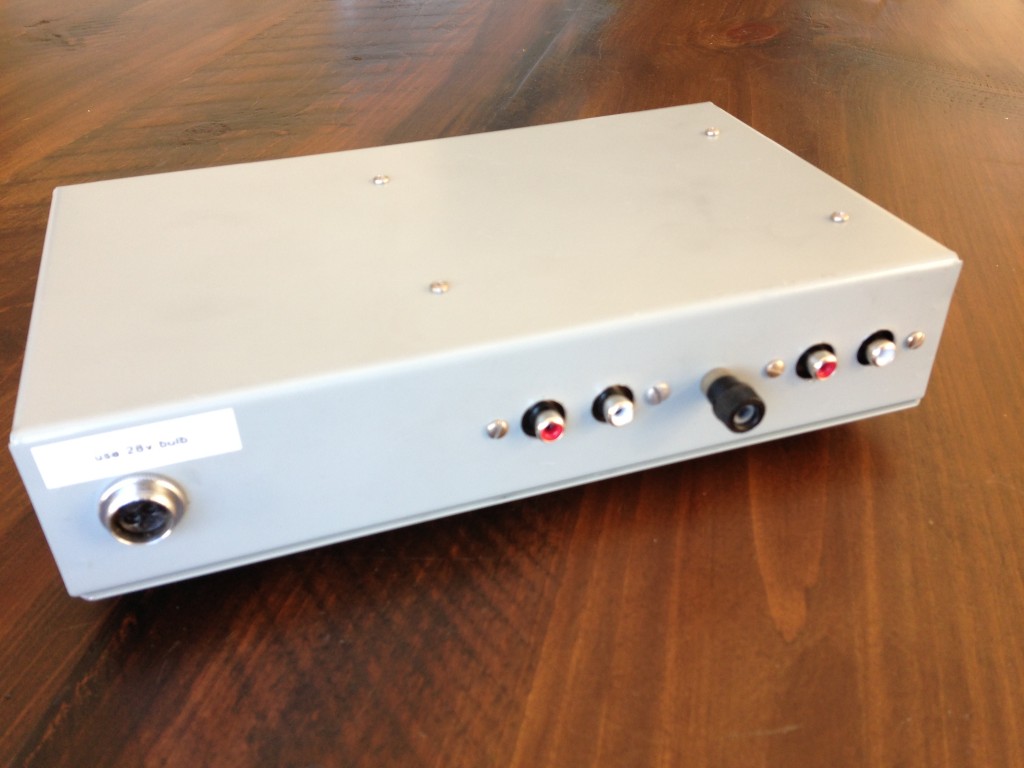 Note that since this thing is running at 24V, I had to try to find a 24v bayonet bulb for the vintage-type jeweled-lamp. Don’t use a 6.3V bulb from yr parts drawer here! It will not end well. Luckily, MCM electronics had 28v bayonet-base bulbs (the closest value that I could find to 24v) for just a few cents. Anyhow, I went through this trouble since I wanted the BHL preamp to match the appearance of the power amp perfectly, but you could easily build this board into whatever you want. Here’s a dude on Instagram who went for more of an ultra-modern/brutalist look for his build. Point is, you can do whatever you like as far as the visual aesthetic yr after. I probably spent about $50 for the non-included components for my build.
Note that since this thing is running at 24V, I had to try to find a 24v bayonet bulb for the vintage-type jeweled-lamp. Don’t use a 6.3V bulb from yr parts drawer here! It will not end well. Luckily, MCM electronics had 28v bayonet-base bulbs (the closest value that I could find to 24v) for just a few cents. Anyhow, I went through this trouble since I wanted the BHL preamp to match the appearance of the power amp perfectly, but you could easily build this board into whatever you want. Here’s a dude on Instagram who went for more of an ultra-modern/brutalist look for his build. Point is, you can do whatever you like as far as the visual aesthetic yr after. I probably spent about $50 for the non-included components for my build.
The circuit is super-simple and it’s very very easy to assemble. The BHL site has a transcript of the directions that come with the kit if yr curious. It took me less than an hour to solder all the parts together. As Jsn explains on his site, “This is just about the simplest circuit possible that will accomplish what we need – reverse-RIAA equalization with gain. This is 2 JFET gain stages with a passive (no feedback) RIAA equalization network sandwiched between them.” Simple as it is, the components included are of a very high quality.
Now, I was replacing a very cheap phono preamp with the BHL (I had been using a $50 Rolls VP29), so keep that in mind – but here were my initial impressions, which the past month of 4-hour-per day listening has proven to be (subjectively) correct:
*The sound is very good; the low end is a bit more even and less ‘rolled off’ versus the ROLLS preamp. Vocal-area midrange is a bit more forward. The high end seems to sound about the same, but the cartridge/LP is probably the limiting factor as far as treble.
*The biggest improvement is that the self-noise of the BHL is so much lower. And there is less hum. So overall there is really a huge difference in terms of background noise, which just brings out so much more detail in the music. And honestly, I never even thought that my ROLLS preamp was noisy until I installed the BHL.
*Gain is a little lower than the ROLLS that it replaced (maybe 2 or 3 dbs). Not ideal, but not a huge deal.
Full disclosure, and maybe this is unnecessary: Jsn provided the kit to me at-cost. That being said, at the street price of $89 I do still think it is a very good value. If yr thinking of testing the waters of Audio DIY (and you like listening to LPs…), I could not think of a better place to start. Jsn is a great guy, and it was his old BHL blog that was one of my greatest inspirations in starting PS dot com; so if you dig this website, support the dude and get yrself some upgraded sound in the process.
Boozhound Labs
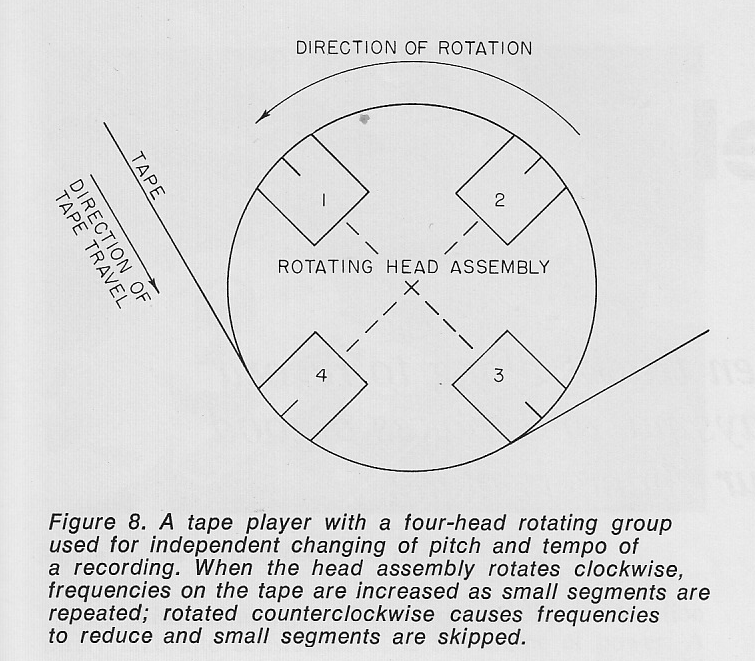
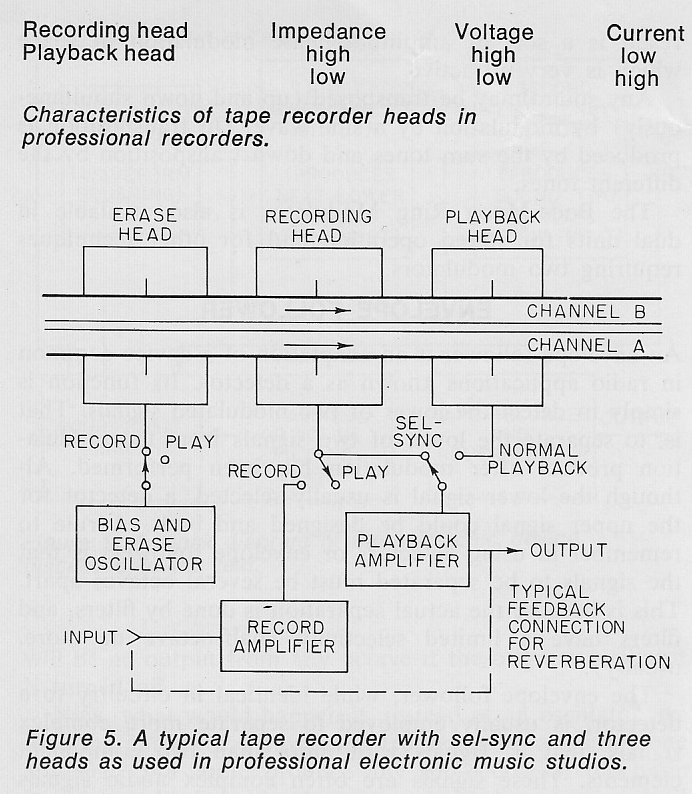
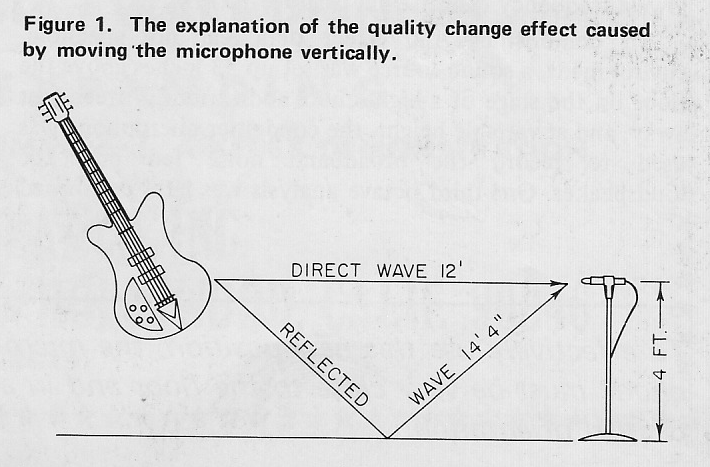
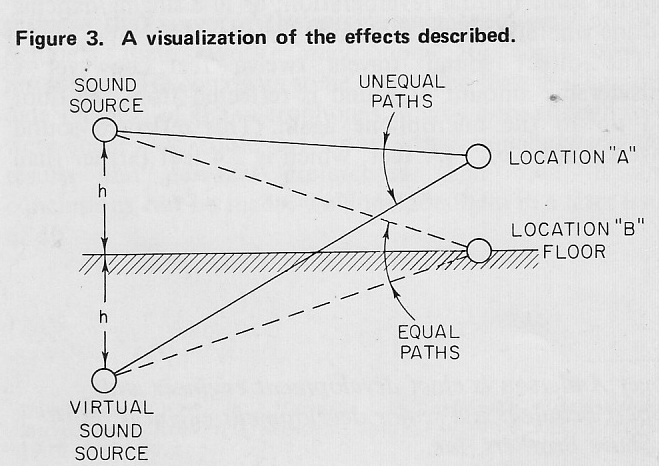
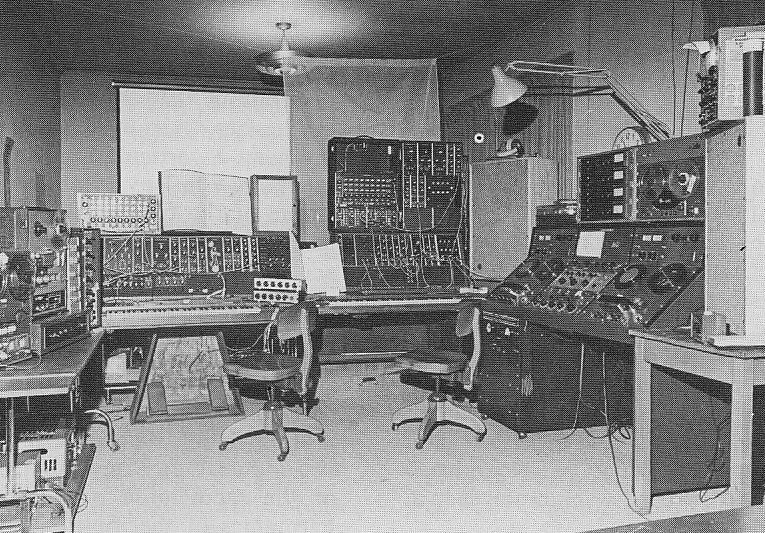 Today on PS dot com: a 1971 article by one Robert C. Ehle on the subject of ‘The Electronic Music Studio.’
Today on PS dot com: a 1971 article by one Robert C. Ehle on the subject of ‘The Electronic Music Studio.’