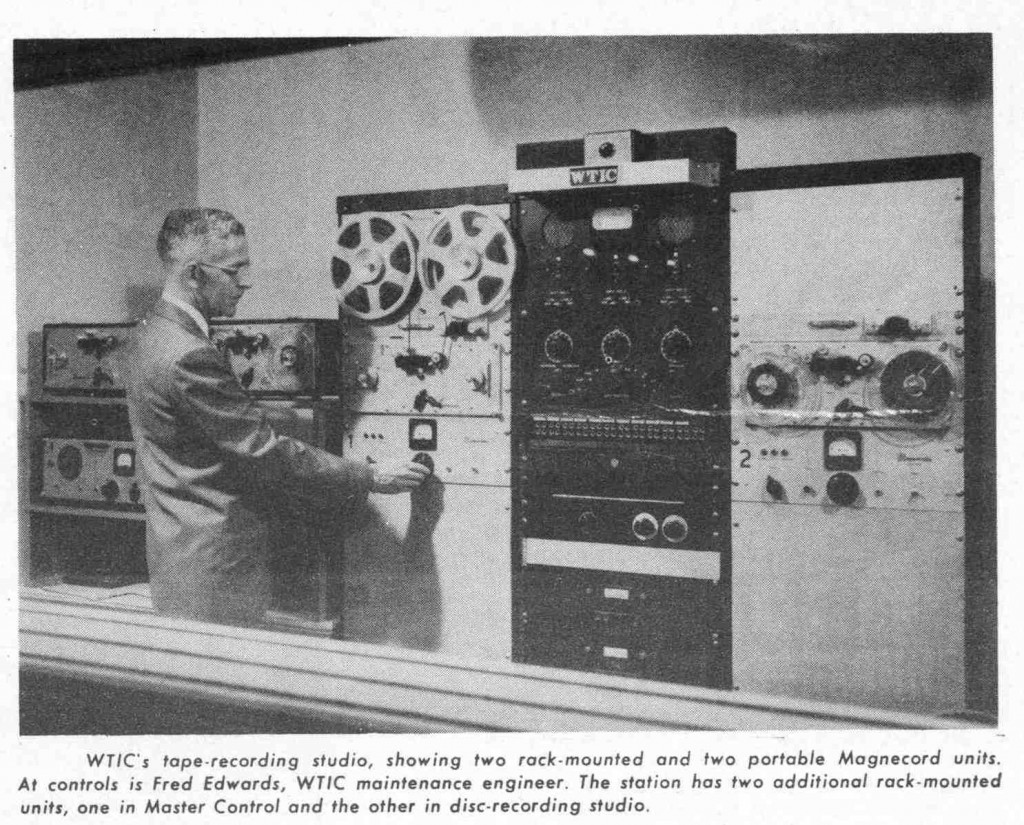
 Continuing the thread from yesterday’s post: here are the 1952 issues of Magnecord, INC. Click on the link to download each issue.
Continuing the thread from yesterday’s post: here are the 1952 issues of Magnecord, INC. Click on the link to download each issue.
 This week we’ll conclude our series of archival material courtesy of Magnecord founding partner John Boyers. John’s son D. graciously scanned every page of every available issue of the company publication “Magnecord INC,” which was published between 1950 and 1954.
This week we’ll conclude our series of archival material courtesy of Magnecord founding partner John Boyers. John’s son D. graciously scanned every page of every available issue of the company publication “Magnecord INC,” which was published between 1950 and 1954.
If anyone out there has any issues that we are missing, please chime in and let’s figure out a way to get them online. Magnecord was a crucial developer of tape-recording and pro-audio hardware whose contributions have been largely forgotten in the modern era. I use a Magnecord PT6 at our studio Gold Coast Recorders to make the occasional ‘old-time’ recording and it’s a testament to the skill of engineers like Mr. Boyers that the machine still works great SIXTY years after it rolled out the Chicago plant.
The ‘Magnecord INC’ publications are fascinating because they reveal the dawn of the high-fidelity audio-recording age. Remember that these (and certain of the AMPEX machines of the era) were portable audio-recorders with 40hz- 15kz frequency response. These facts opened up world of possibility for audio capture. Reading through these old issue of “Magnecord INC” opens the door to a time when the world was first figuring out all of the things that could be done with a portable machine that could capture and playback sound to the near-limits of human hearing ability. Many of the then-novel tape-recording tasks described in these publications may seem mundane; but many are surprising and quite odd applications which never really caught on past a few enthusiastic early-experimenters.
Without further ado, here are the issue from 1950. More to follow tomorrow. Download and enjoy.
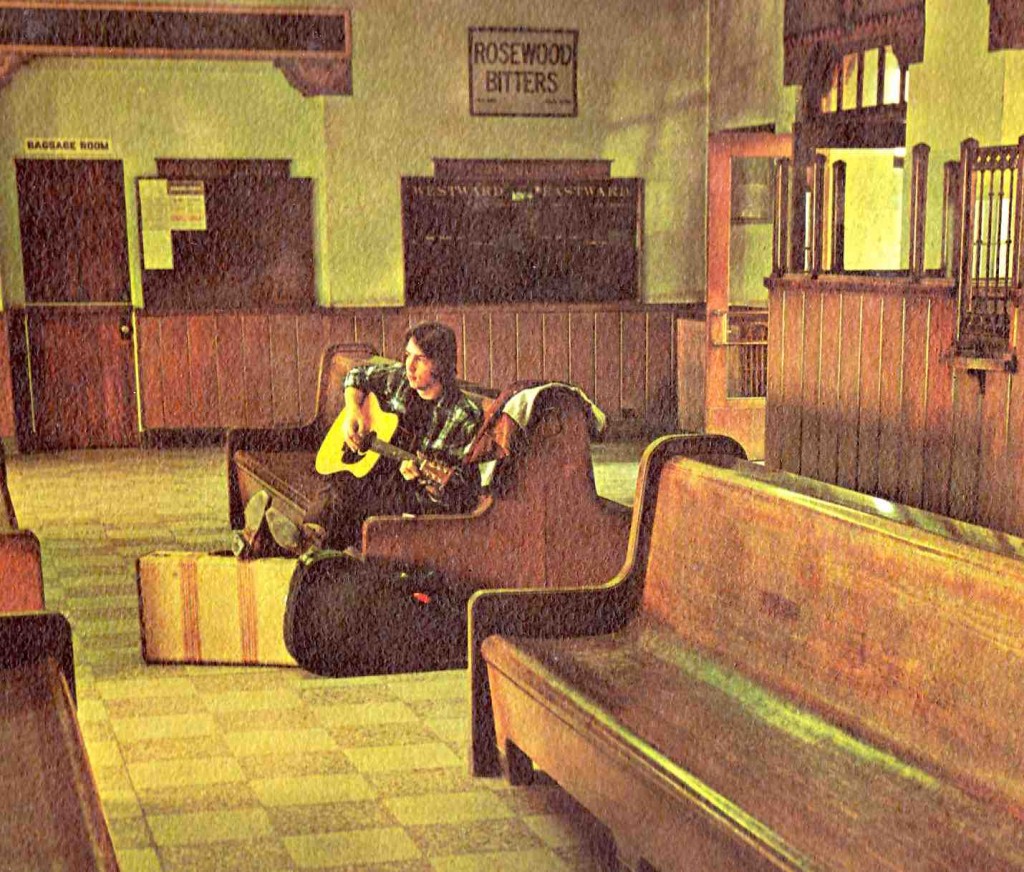
Better Living Through Auto-Reverse
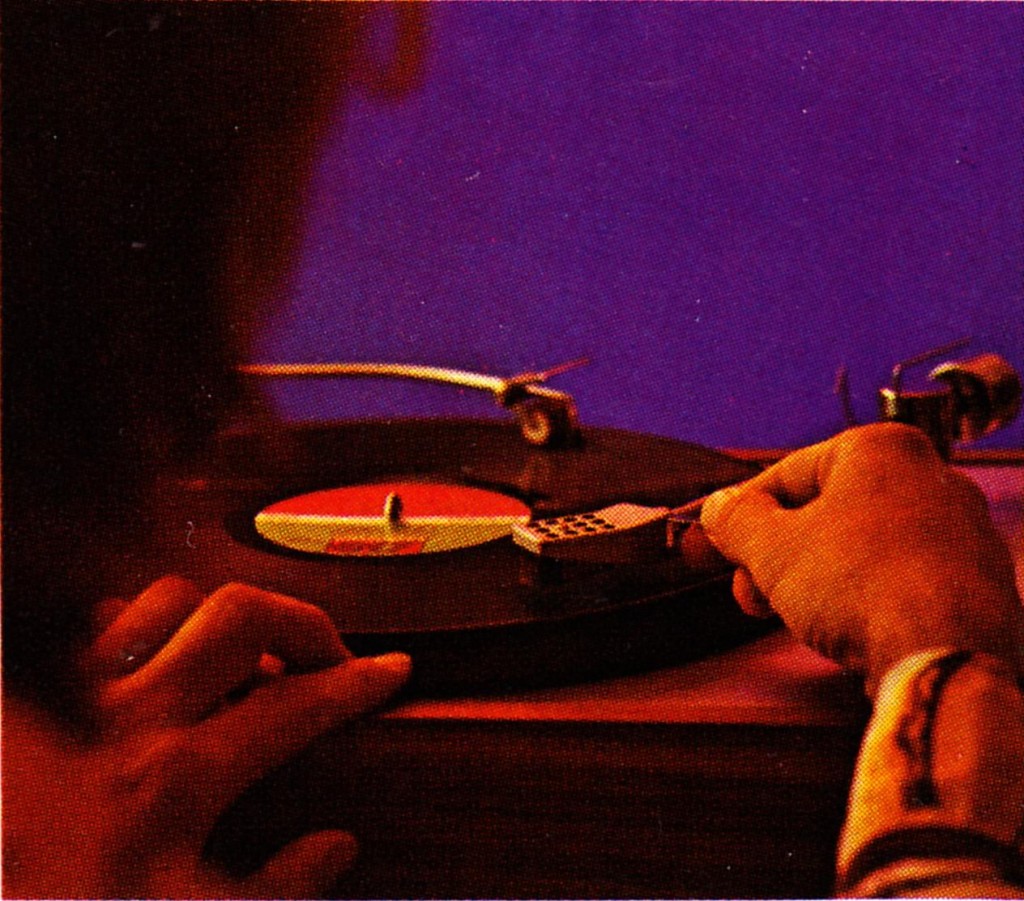 Well alright… Cheryl from the Madison office is finally coming over to the condo for dinner. I think she said she liked John Denver and Jim Croce…
Well alright… Cheryl from the Madison office is finally coming over to the condo for dinner. I think she said she liked John Denver and Jim Croce…
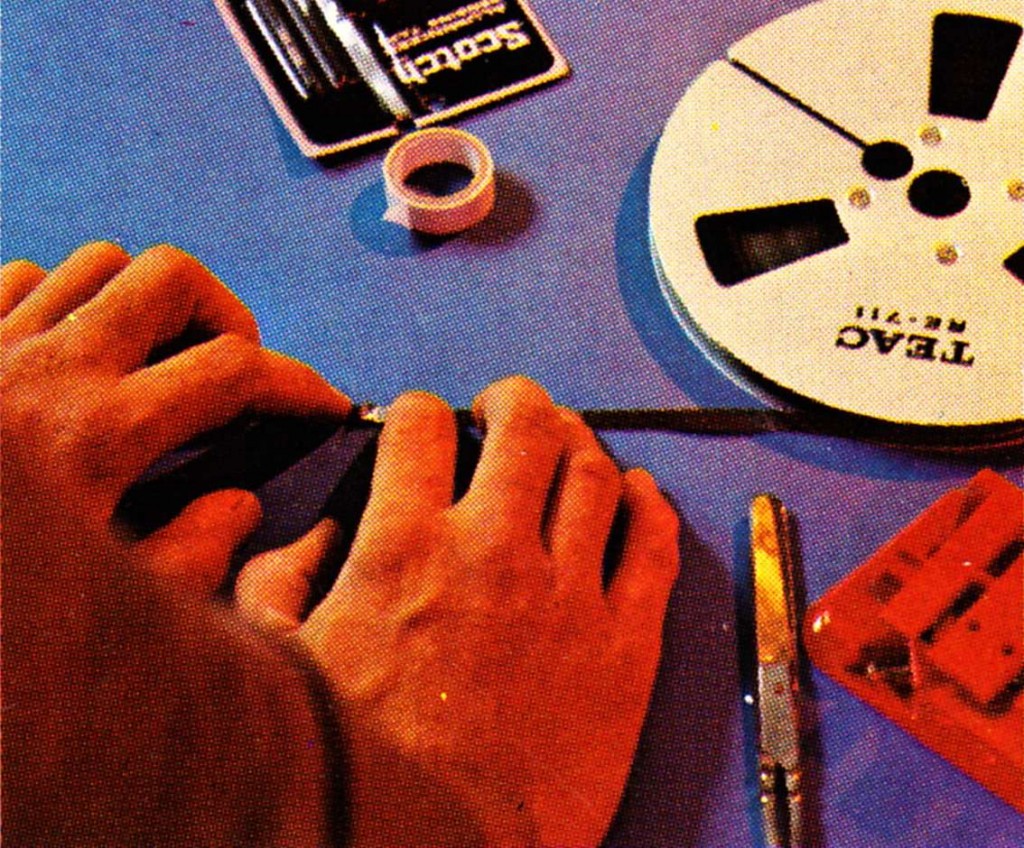 Gonna make pretty much the ultimate mix… man this is really gonna set the mood…
Gonna make pretty much the ultimate mix… man this is really gonna set the mood…
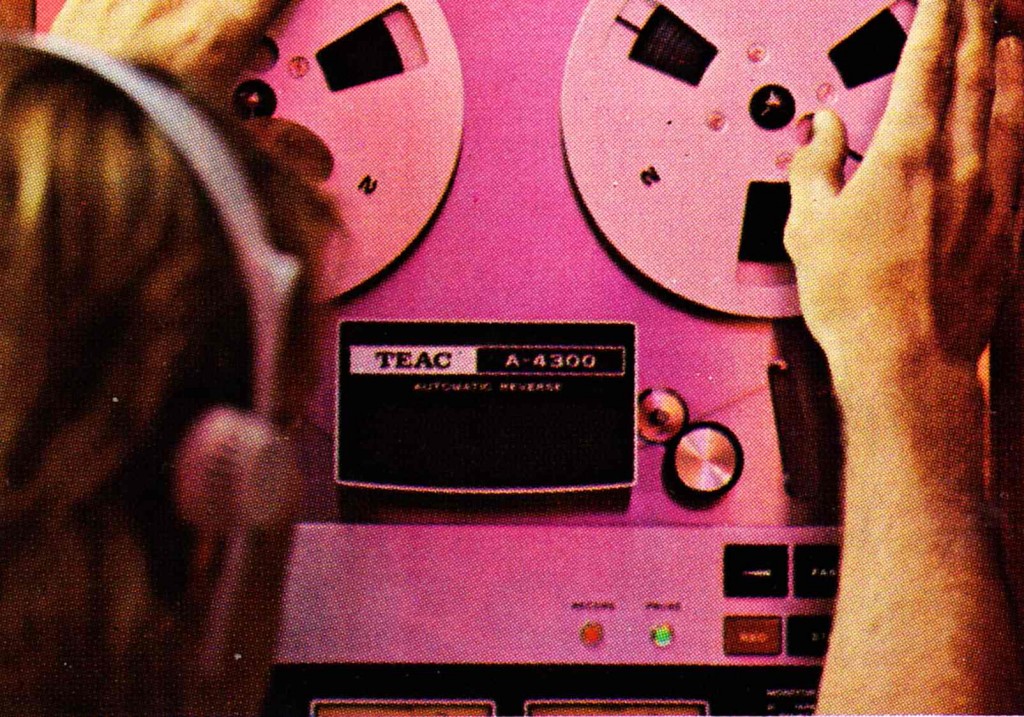 OK it’s almost 8… let’s get this tape up on the deck. Thanks to TEAC Auto-Reverse technology, the tape will play over and over and over and over again all night, regardless of how long the night ends up being.
OK it’s almost 8… let’s get this tape up on the deck. Thanks to TEAC Auto-Reverse technology, the tape will play over and over and over and over again all night, regardless of how long the night ends up being.
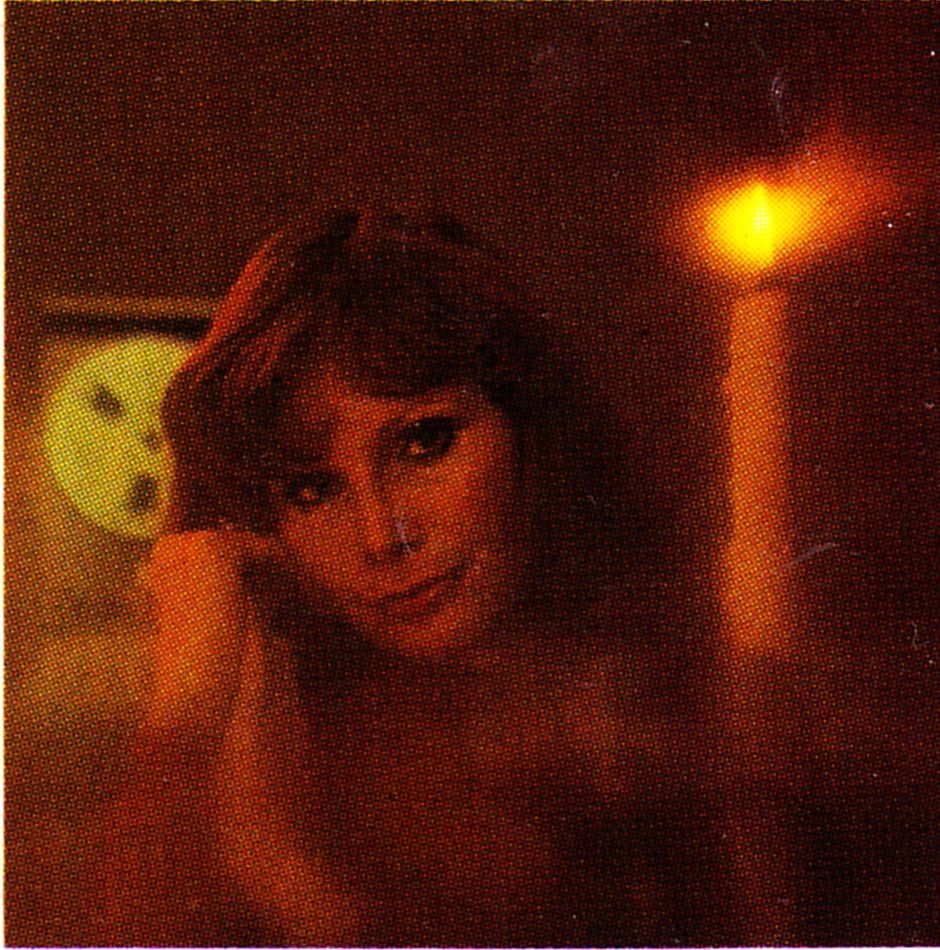 What a fox. Oh yeah? Like the music? Yeah I love these guys too… Saw them at the OysterFest a few years ago… oh yeah, glad you dig it…
What a fox. Oh yeah? Like the music? Yeah I love these guys too… Saw them at the OysterFest a few years ago… oh yeah, glad you dig it…
*******
***
 I am not making any of this up. This is an actual TEAC print-ad from January 1976. It features single-people in their mid-30s having a romantic evening at the gentleman’s home (condo). The selling proposition of this product is ‘Auto-Reverse,’ AKA, you don’t have to flip the tape over when the side ends. When we were growing up in the cassette-tape era, Auto-Reverse was still a premium-feature of the higher-priced tape players. I actually don’t think I ever had an auto-reverse walkman; they were just too expensive. Flipping the tape was just part of life. Good thing i was too young at the time to have any ladies to entertain. By the time I started dating, the CD was already in-play. ‘Repeat’ is of course a feature of all CD decks.
I am not making any of this up. This is an actual TEAC print-ad from January 1976. It features single-people in their mid-30s having a romantic evening at the gentleman’s home (condo). The selling proposition of this product is ‘Auto-Reverse,’ AKA, you don’t have to flip the tape over when the side ends. When we were growing up in the cassette-tape era, Auto-Reverse was still a premium-feature of the higher-priced tape players. I actually don’t think I ever had an auto-reverse walkman; they were just too expensive. Flipping the tape was just part of life. Good thing i was too young at the time to have any ladies to entertain. By the time I started dating, the CD was already in-play. ‘Repeat’ is of course a feature of all CD decks.
Anyhow, this advert is a good example of the ‘lifestyle-benefit’ advertising that consumer electronics manufacturers employed in the 70’s. Set a little stage, tell a little story, allow the consumer to insert themselves into the scenario. This was in some contrast to much electronics advertising of the 40s to 60s, much of which was focused on ‘fidelity’ and ‘value.’ By the 70s, 20-20k performance (OK, 30-15k) was a given in most equipment; transistors and PCBs had made this stuff affordable to most working-class folks; so the benefit of one brand over the other needs to be demonstrated in other ways. In this case, the increased romantic-potential of a dinner-date.
Gibson Guitar Amplifers: 1966
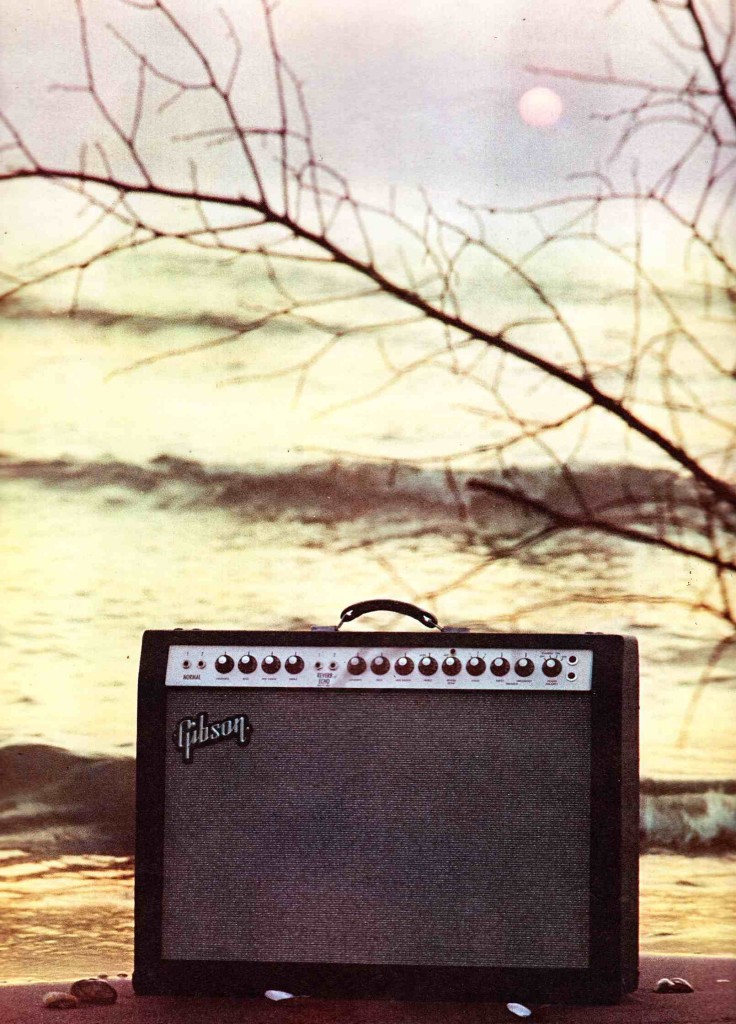 Download a twelve-page scan of the entire guitar-amp line represented in Gibson’s 1966 catalog:
Download a twelve-page scan of the entire guitar-amp line represented in Gibson’s 1966 catalog:
DOWNLOAD: Gibson_amps_1966
Models covered, with specs and photos, include: Gibson GSS-100, GSS-50, and PLUS-50 solid-state amplifiers; Gibson Titan, Mercury, Atlas, and Atlas Medalist (Bass) amps; Vanguard GA-77, Apollo GA-95, Multi-stereo GA-79, Ranger GA-66, and Saturn GA-45 Reverb/Tremolo amps; Lancer GA-35, Minuteman GA-20 RVT, Explorer GA-15 RVT, Recording GA-75 and GA-75L, Skylark GA-5 and GA-5T practice/studio amps.
 Above is some of the most awful product-prose that I have ever encountered, taken directly from p.16 of the 1966 catalog. ‘Butterflies, Stroking, Squeezing the full measure …..’ Were these people fucking high? Actually, the problem is that they probably weren’t high. Yet. 1966 seems to have been a decisive year in musical-instrument marketing; the very last year that manufacturers denied the very existence of Rock and Roll. Most of the catalogs and advertisements from 1966 (and earlier) were very staid, grown-up, and had a romantic rather than… aquarian… sensibility. In 1967 we start to see the bright colors, bold graphic design, and general emphasis on youth that remain in most musical-instrument marketing even today.
Above is some of the most awful product-prose that I have ever encountered, taken directly from p.16 of the 1966 catalog. ‘Butterflies, Stroking, Squeezing the full measure …..’ Were these people fucking high? Actually, the problem is that they probably weren’t high. Yet. 1966 seems to have been a decisive year in musical-instrument marketing; the very last year that manufacturers denied the very existence of Rock and Roll. Most of the catalogs and advertisements from 1966 (and earlier) were very staid, grown-up, and had a romantic rather than… aquarian… sensibility. In 1967 we start to see the bright colors, bold graphic design, and general emphasis on youth that remain in most musical-instrument marketing even today.
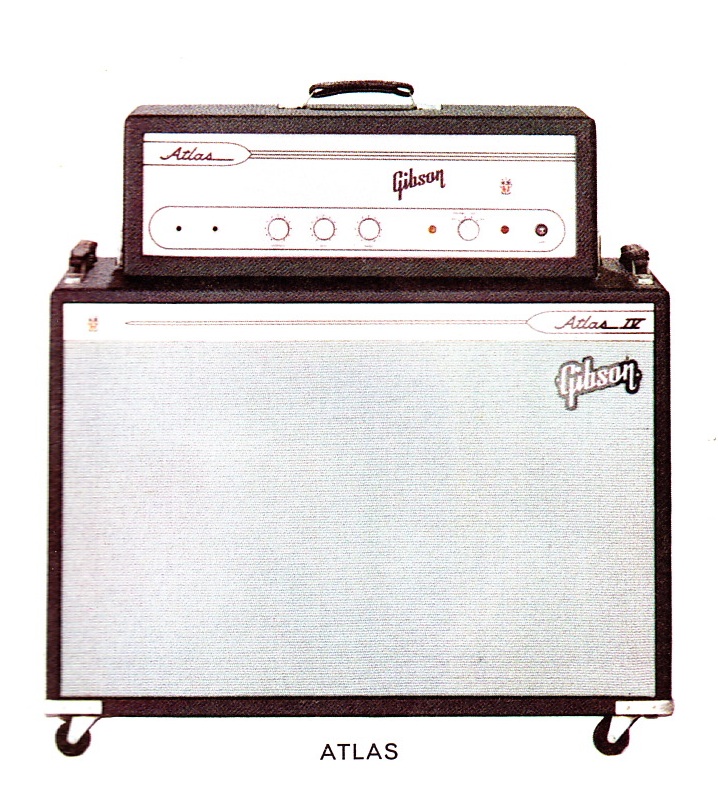 Above, the Gibson Atlas. What a beautiful piece of industrial design this is. After I came across this catalog, I looked for any examples of this unit for sale. I could not find a single one. While I am sure that the Gibson Atlas did not ship in nearly the same numbers as, say, a Fender Bassman, there is another reason that these 60’s Gibson amps are not too common today: reliability and build quality. While Gibson amps of the 1940s-60s are excellent sounding in general, Leo Fender really had these midwesterners beat as far as construction quality. Earlier this month I serviced a couple of early 60s Gibsons for a client. Opening up a mint-condition Gibson circa ’62 student amp… I can’t recall the model, but it was a PP 6AQ5 amp with fixed-depth trem… anyway, opened it up to find a few haphazardly placed terminal strips, and even a few multi-component junctions meeting in mid-air. This is in sharp contract to the build of even the cheapest Fenders, all of which have carefully laid-out, serviceman-friendly terminal boards. The same construction techniques you will find in much military and commercial hardware of the pre-PCB age. This is not surprising when you remember that Leo Fender began his career as a radio repairman rather than as a luthier or musician. As you (IF you) learn to design and build tube audio equipment, take some time to open up as many old pieces of hardware as you can find. $2, $5 pieces… old test equipment, radios, organs… check out the construction and mounting techniques, lead dress, solder joints… you will find a huge variety of techniques used, all of which will have some useful applications in your own work. This is all the stuff that can’t learn from schematics, and certainly not from reading (blogs) online.
Above, the Gibson Atlas. What a beautiful piece of industrial design this is. After I came across this catalog, I looked for any examples of this unit for sale. I could not find a single one. While I am sure that the Gibson Atlas did not ship in nearly the same numbers as, say, a Fender Bassman, there is another reason that these 60’s Gibson amps are not too common today: reliability and build quality. While Gibson amps of the 1940s-60s are excellent sounding in general, Leo Fender really had these midwesterners beat as far as construction quality. Earlier this month I serviced a couple of early 60s Gibsons for a client. Opening up a mint-condition Gibson circa ’62 student amp… I can’t recall the model, but it was a PP 6AQ5 amp with fixed-depth trem… anyway, opened it up to find a few haphazardly placed terminal strips, and even a few multi-component junctions meeting in mid-air. This is in sharp contract to the build of even the cheapest Fenders, all of which have carefully laid-out, serviceman-friendly terminal boards. The same construction techniques you will find in much military and commercial hardware of the pre-PCB age. This is not surprising when you remember that Leo Fender began his career as a radio repairman rather than as a luthier or musician. As you (IF you) learn to design and build tube audio equipment, take some time to open up as many old pieces of hardware as you can find. $2, $5 pieces… old test equipment, radios, organs… check out the construction and mounting techniques, lead dress, solder joints… you will find a huge variety of techniques used, all of which will have some useful applications in your own work. This is all the stuff that can’t learn from schematics, and certainly not from reading (blogs) online.
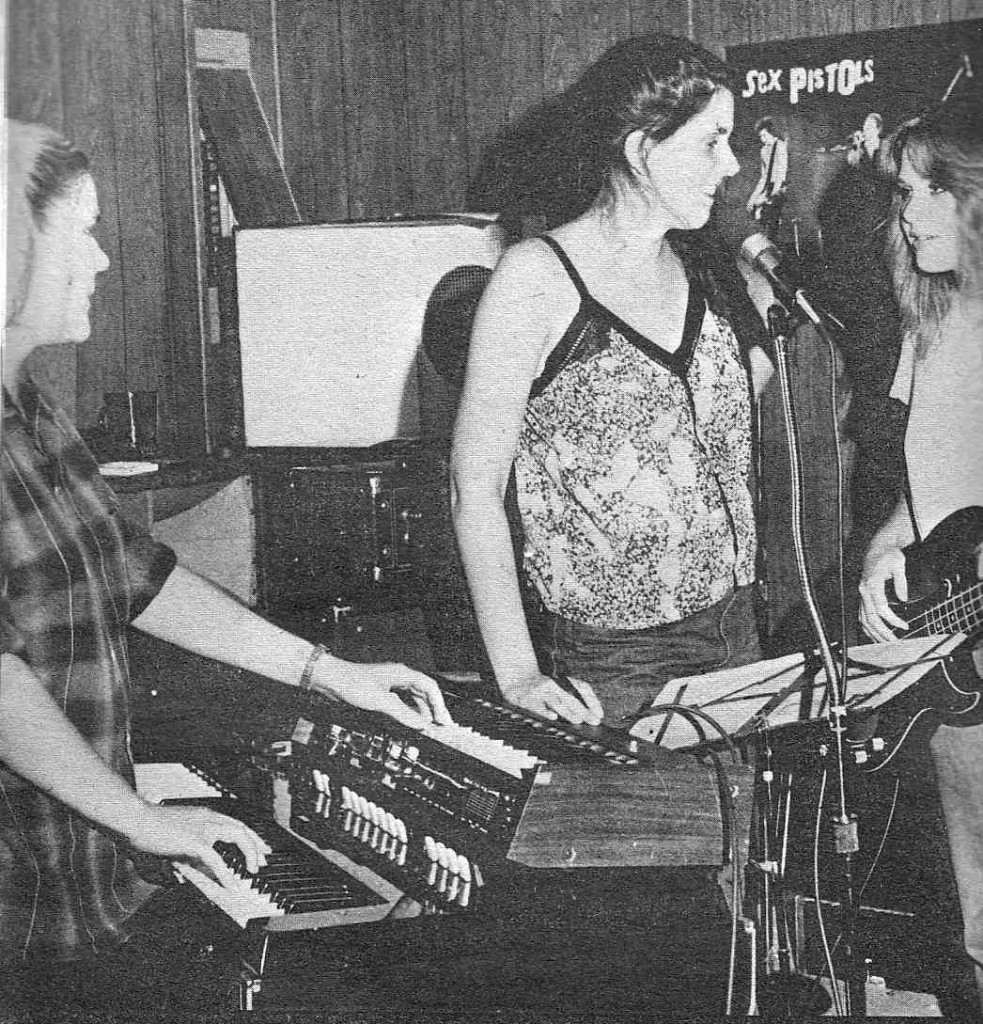
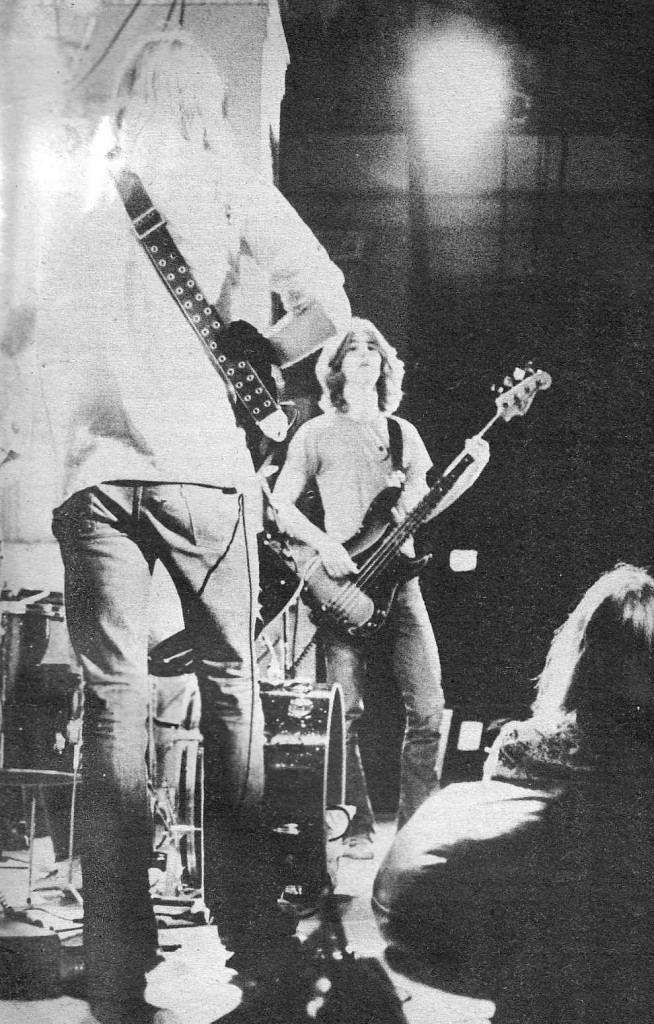
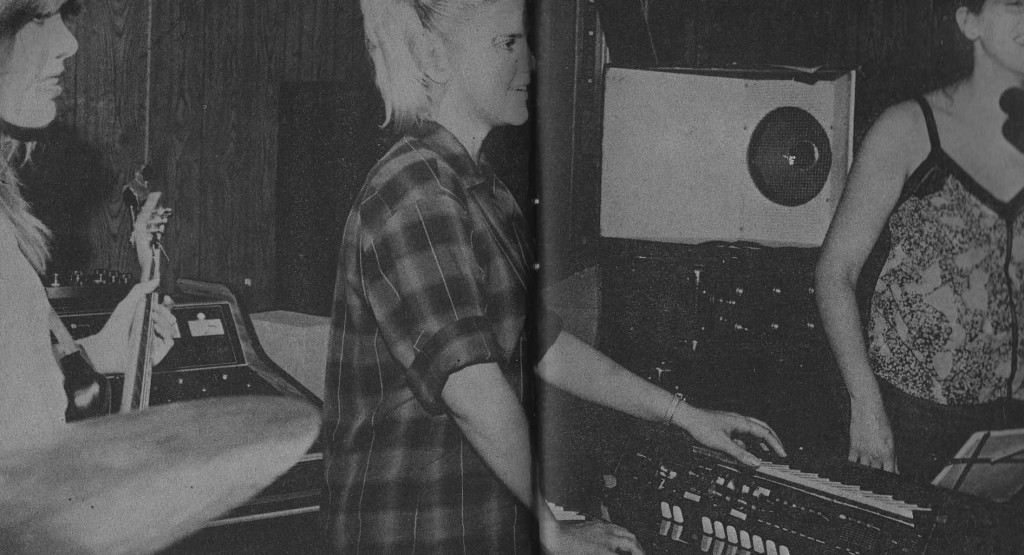
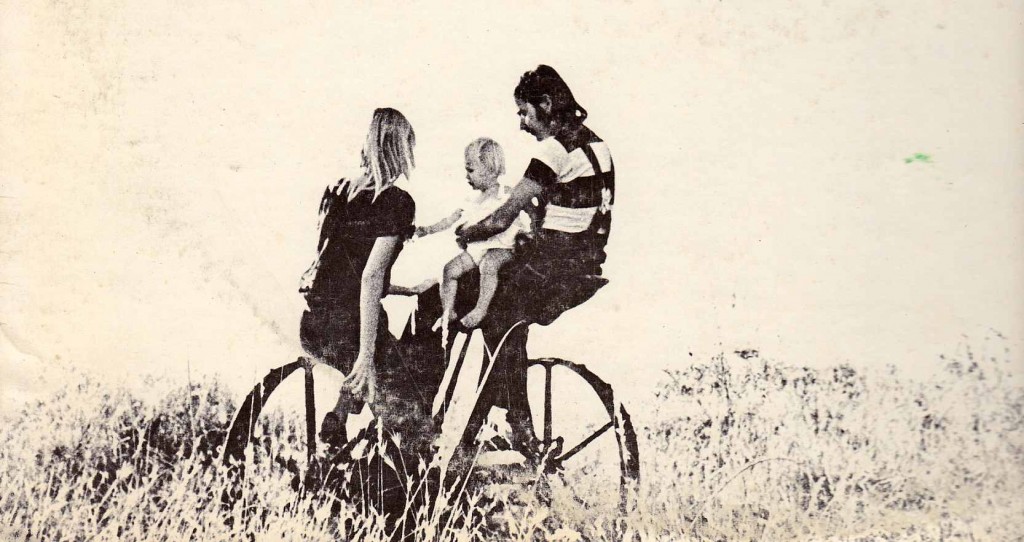
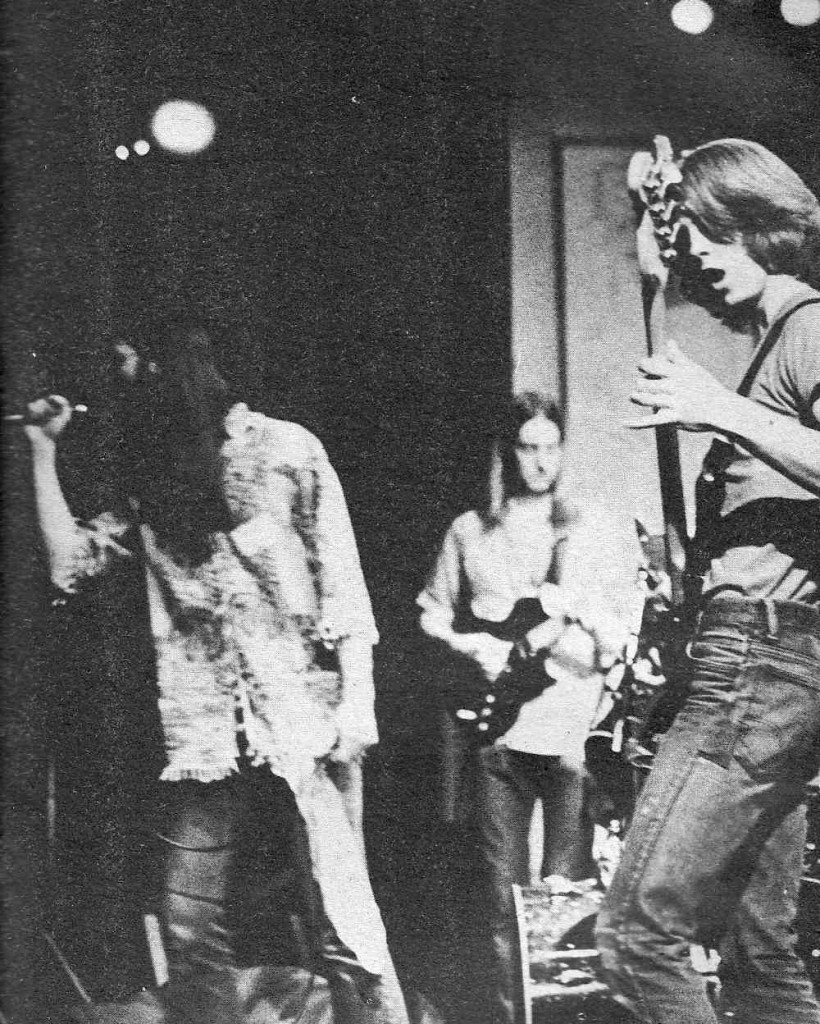 Ah salad days.
Ah salad days.
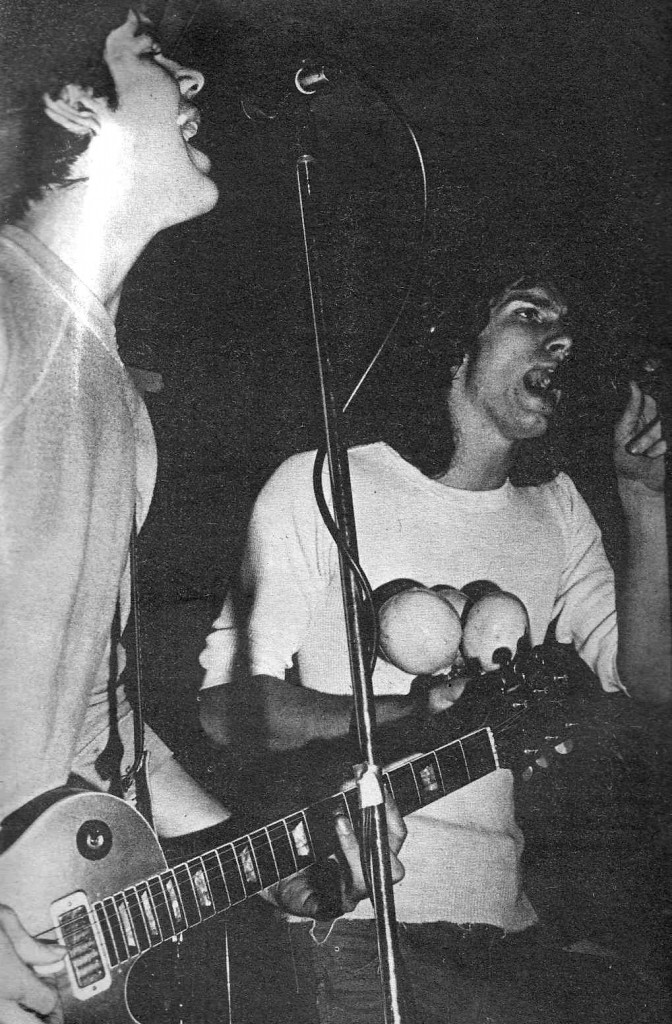
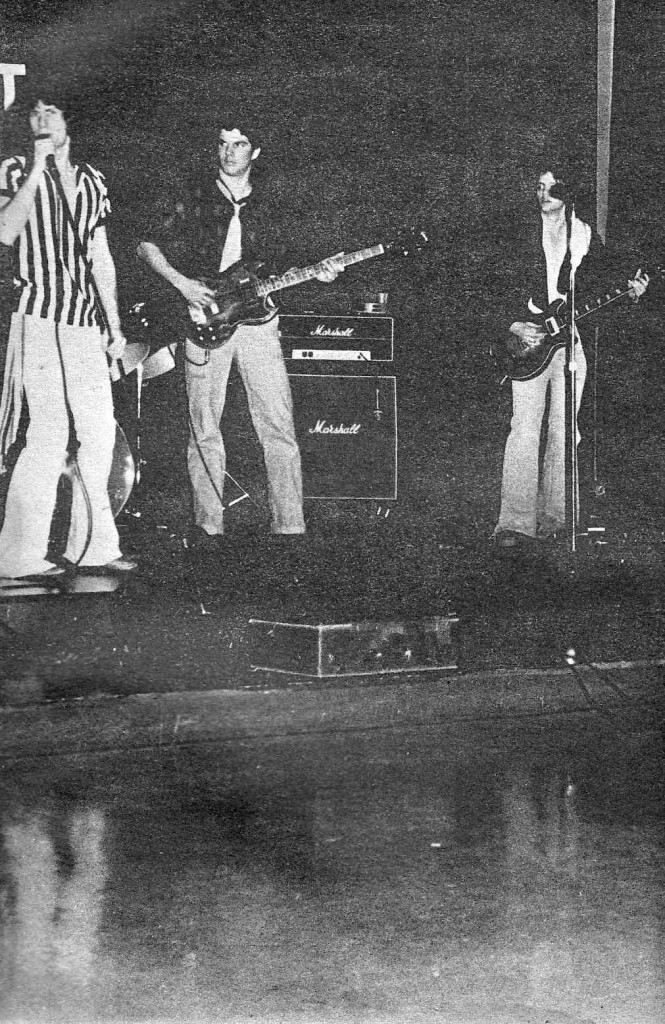
 Making noise with some high-school bros
Making noise with some high-school bros
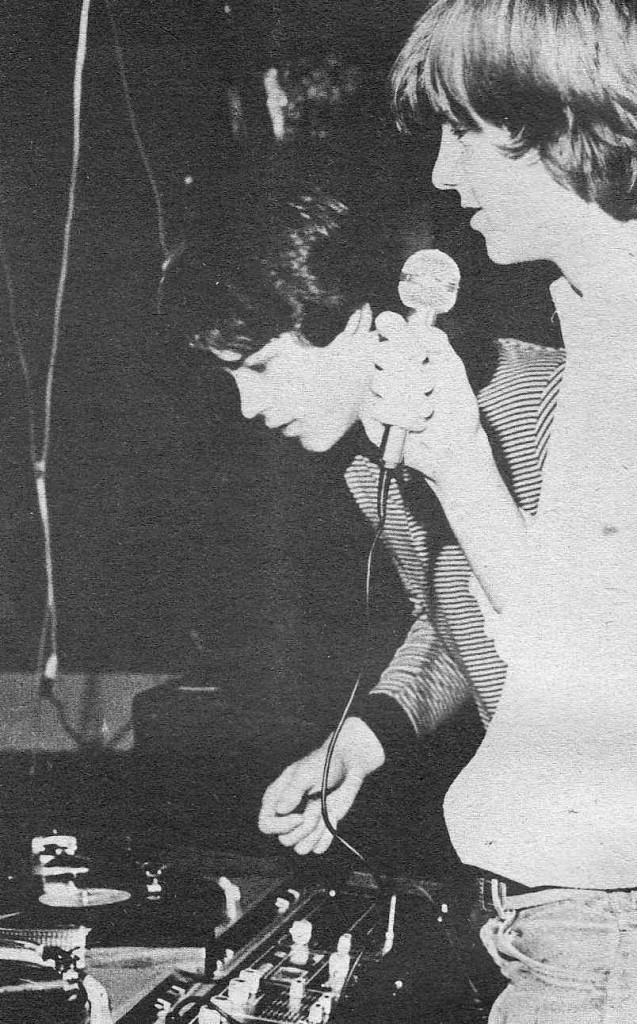 maybe you were on the “wheels-of-steel”
maybe you were on the “wheels-of-steel”
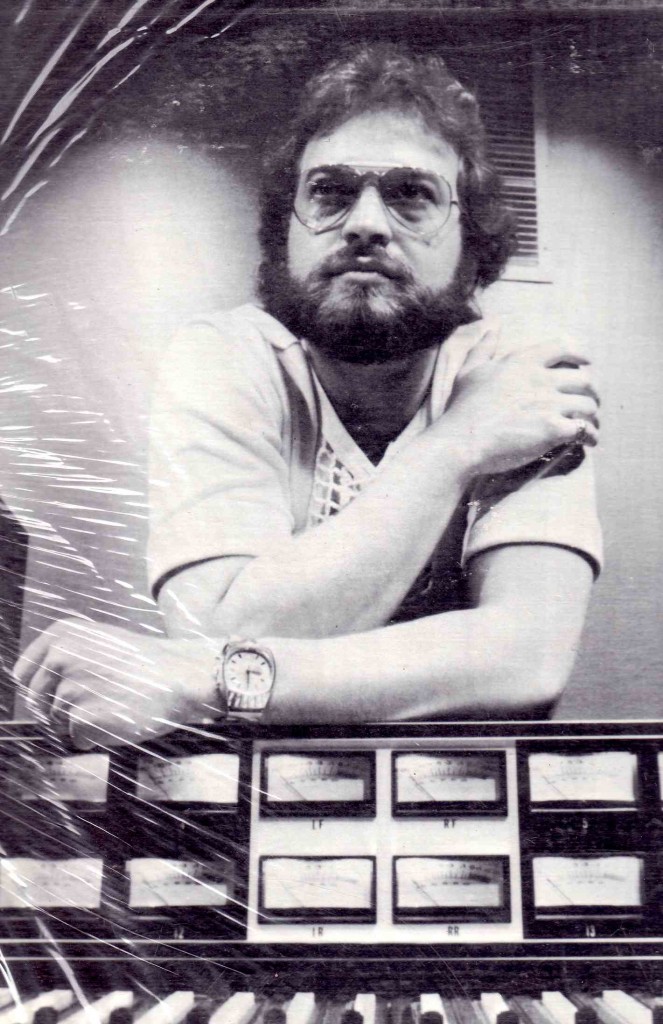
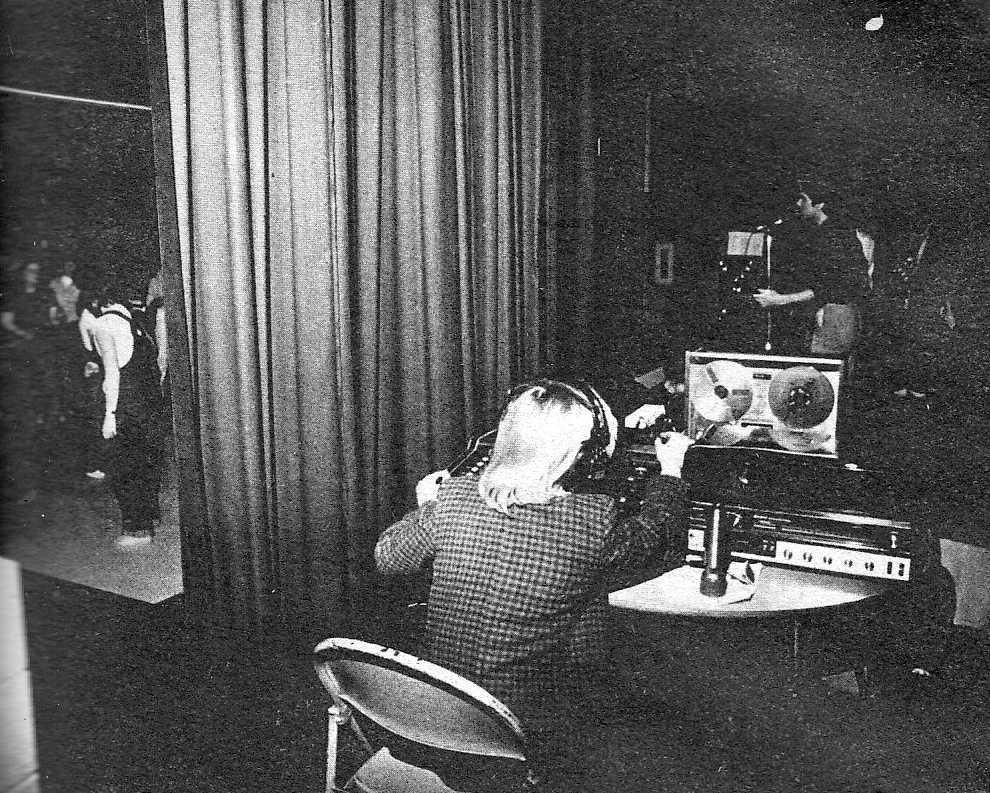 or maybe you were the one who pushed ‘RECORD’ while others were in the lights
or maybe you were the one who pushed ‘RECORD’ while others were in the lights
 “Starting your own band” (h.f. ‘SYOB’) was published in paperback by Weekly Reader Books of Middletown CT in 1980. It’s the work of one Lani Van Ryzin, who also wrote several other books on subjects and near as “Cutting a Record in Nashville” and as far as one volume on creating magical spaces in your yard. Anyhow, SYOB is a 64pp volume squarely aimed at high-school students. Some of the suggestions on offer:
“Starting your own band” (h.f. ‘SYOB’) was published in paperback by Weekly Reader Books of Middletown CT in 1980. It’s the work of one Lani Van Ryzin, who also wrote several other books on subjects and near as “Cutting a Record in Nashville” and as far as one volume on creating magical spaces in your yard. Anyhow, SYOB is a 64pp volume squarely aimed at high-school students. Some of the suggestions on offer:
“To succeed, (a band) must flow together– not just musically, but in feelings, too. And it simply won’t flow if’s full of personality hassles…”
“It’s probably best not to start talking ‘Band Talk’ until after several jam sessions.”
“Extension cords are expensive and necessary…”
“Making music is making sounds, and the quality of the sound you make is critical.”
Could there ever really be a book of a sufficient length to offer the knowledge necessary to operate a rock-band smoothly? The answer is no. Lani, if you’re out there, tell us about the bands you were in… send us some MP3s.
Back to the photos. I am going to wishfully believe that these pics were shot in Connecticut, home of the publishing company responsible for this treatise… prove me wrong (or right). As I look at these images, which truly feel like they are from so-very-long-ago, I have to recognize that I was in a high-school garage-band in CT a mere 10 years later. Trying not to cross the line from ‘historical research’ to ‘actual nostalgia.’ Wish me luck.
 Download a five-page scan of the various guitar amps, guitars, effects, and other Rock-combo-flotsam available from Heathkit in 1969:
Download a five-page scan of the various guitar amps, guitars, effects, and other Rock-combo-flotsam available from Heathkit in 1969:
DOWNLOAD: Heathkit_guitar_amps_1969
Products on offer include: Heathkit Starmaker TA-16 amplifier; AKG and Shure mics and Atlas stands; TA-27 guitar amp; Harmony ‘Silhouette’ H17 electric guitar; Heathkit TA-28 “Fuzz” Booster and TA-58 headphone amp; TA-17 amplifier head and TA-17-1 speaker system; TA-38 bass amplifer (130 lbs!); and a kit version of the famous Vox Jaguar organ.

M. and I were digging through some local pawn shops last week and we spotted the above-depicted ‘Starmaker’ amplifer buried under some radial arm saws. Coincidentally enough, the price they were asking was the same $119 that it would have cost you to buy as a kit in 1969. “…in about 8-10 hours and you’ll have the best value around in a solid-state amp. Order yours now.”
 Kit-built electronics were a fascinating and vital part of consumer-culture in America through the 1970s. It’s kind of liberating when you think about it: a product which parses out some (but certainly not all) of the labor from the physical materials of the product; you, the consumer, can then create the finished product from a combination of your capital (money) and your raw labor/time. I am about to do the same thing with a shed; we need someplace to put our lawnmower, and the right balance of capital/labor for my particular circumstances is a shed-kit. I have neither the money to pay someone to build a shed for me nor the free time to build a shed from a blueprint and a pile of uncut lumber; the shed kit seems like the right choice for me. At some point in America, the value of the labor required to complete a piece of consumer-electronics equipment fell below a certain point, thanks to a combination automation (robots) and cheap foreign labor. This made the Heathkit a fairly indefensible option. This affordability of foreign labor (and transportation costs…) can’t last forever though. So I have to wonder: as foreign labor prices continue to rise, will we ever see a return of the kit-option for consumer electronics in America?
Kit-built electronics were a fascinating and vital part of consumer-culture in America through the 1970s. It’s kind of liberating when you think about it: a product which parses out some (but certainly not all) of the labor from the physical materials of the product; you, the consumer, can then create the finished product from a combination of your capital (money) and your raw labor/time. I am about to do the same thing with a shed; we need someplace to put our lawnmower, and the right balance of capital/labor for my particular circumstances is a shed-kit. I have neither the money to pay someone to build a shed for me nor the free time to build a shed from a blueprint and a pile of uncut lumber; the shed kit seems like the right choice for me. At some point in America, the value of the labor required to complete a piece of consumer-electronics equipment fell below a certain point, thanks to a combination automation (robots) and cheap foreign labor. This made the Heathkit a fairly indefensible option. This affordability of foreign labor (and transportation costs…) can’t last forever though. So I have to wonder: as foreign labor prices continue to rise, will we ever see a return of the kit-option for consumer electronics in America?

 Do you ever come across a Vox Jaguar and wonder why it does not work quite right? Well now we know: it could have originated as one of these kits; 91 lbs of cold solder joints and sloppy lead dress. Heathkit makes a bold claim about the capability of the above Jaguar when used in league with their TA-38 bass amp: “Here’s a combination that will produce the most mind-bending, soul-grabbing sound around.” 266 lbs, $499.00.
Do you ever come across a Vox Jaguar and wonder why it does not work quite right? Well now we know: it could have originated as one of these kits; 91 lbs of cold solder joints and sloppy lead dress. Heathkit makes a bold claim about the capability of the above Jaguar when used in league with their TA-38 bass amp: “Here’s a combination that will produce the most mind-bending, soul-grabbing sound around.” 266 lbs, $499.00.
Keyboard accessories circa mid 70s
 The ACOUSTIC Model 500 ‘Keyboard Control Center.’ Never seen this piece before. The original ACOUSTIC amps from the early 70s are really not-terrible solid-state amps. We used one back in high school for the Rhodes and it was pretty excellent.
The ACOUSTIC Model 500 ‘Keyboard Control Center.’ Never seen this piece before. The original ACOUSTIC amps from the early 70s are really not-terrible solid-state amps. We used one back in high school for the Rhodes and it was pretty excellent.
 The Komplete Kustom lineup from their sadder post-Naugahyde era. See this link for a detailed discussion of the earlier, more iconic Kustom pieces.
The Komplete Kustom lineup from their sadder post-Naugahyde era. See this link for a detailed discussion of the earlier, more iconic Kustom pieces.
 The Powerhouse Rhythm Unit, an infinite-loop tape cartridge playback system designed to do the work of a drum machine.
The Powerhouse Rhythm Unit, an infinite-loop tape cartridge playback system designed to do the work of a drum machine.
 The WMS Interphaser, a phase-shift pedal from a small maker.
The WMS Interphaser, a phase-shift pedal from a small maker.
Nothing too exciting today… just a few odds and ends that caught my eye.
Thanks to Steve DiCostanzo and WPKN 89.5 FM in Bridgeport CT for inviting me on-air for two hours last night to present a program that I call “The Devil in God’s House: Gospel Music themes in RockNRoll of the Nixon Era.” The show was live last night 6/13 from 10PM til midnight.
Summer 2011
Keys of the 70s
 Strings & Things Memphis advert for keyboards circa 1977.
Strings & Things Memphis advert for keyboards circa 1977.
Been looking through some mid-70s issues of “Contemporary Keyboard” (h.f. “CK”) magazine. CK later became simply “Keyboard,” which is still in publication; it’s part of the GUITAR PLAYER family of publications. NEways… 1976/7 was an interesting time in the development of keyboard instruments. Affordable polyphonic (IE., you can play more than one note at a time) synthesizers were still a few years away, and realistic-sounding electronic pianos were still about a decade away. So what you had was a very mixed bag of Electronic Pianos and ‘String Synthesizers,’ which are both basically hyped-up electric organs; some still-useful electro-acoustic instruments; and a pretty wide range of pretty experimental synthesizers, many from small manufacturers that didn’t stay around very long. In about 6 years this would all be blown away by advanced Japanese synths with built-in programming, patch memory, and all with polyphony; the Roland/Korg/Yamaha DX7 era; and this too would fall at the hands of the dreaded Korg M1, which ushered in the Rompler era. Anyone out there using an M1 lately?
 The ARP pro-soloist, typical of the ‘preset’ synths of the era; preset synths offered interfaces optimized for live-performance rather than endless tweaking in the studio.
The ARP pro-soloist, typical of the ‘preset’ synths of the era; preset synths offered interfaces optimized for live-performance rather than endless tweaking in the studio.


 The Hohner Clavinet, HIP II, and Stringvox. The Clavinet has attained classic status, and many are still in use; not so sure about the HIP II and Stringvox.
The Hohner Clavinet, HIP II, and Stringvox. The Clavinet has attained classic status, and many are still in use; not so sure about the HIP II and Stringvox.

 A couple of Moogs from different ends of the spectrum. The Minitmoog was a ‘preset’ synth; the Polymoog was not a true synth; it was closer to an organ in terms of its basic operating principle.
A couple of Moogs from different ends of the spectrum. The Minitmoog was a ‘preset’ synth; the Polymoog was not a true synth; it was closer to an organ in terms of its basic operating principle.
 A few Paia synth-kit offerings of the mid 70s: the Surf Synthesizer, The Gnome, and the classic 4700. See this link for previous PAIA coverage on PS dot com.
A few Paia synth-kit offerings of the mid 70s: the Surf Synthesizer, The Gnome, and the classic 4700. See this link for previous PAIA coverage on PS dot com.
 An advert for the Polyfusion System A. See this link for previous coverage of the Polyfusion line.
An advert for the Polyfusion System A. See this link for previous coverage of the Polyfusion line.
 The RMI Electra Piano. When we were growing up in the late 80s/early 90s, ‘electric pianos’ like these were about fifty bucks or less; no one wanted them, and that has not changed. They sound pretty awful but they’re still heavy and cumbersome!
The RMI Electra Piano. When we were growing up in the late 80s/early 90s, ‘electric pianos’ like these were about fifty bucks or less; no one wanted them, and that has not changed. They sound pretty awful but they’re still heavy and cumbersome!
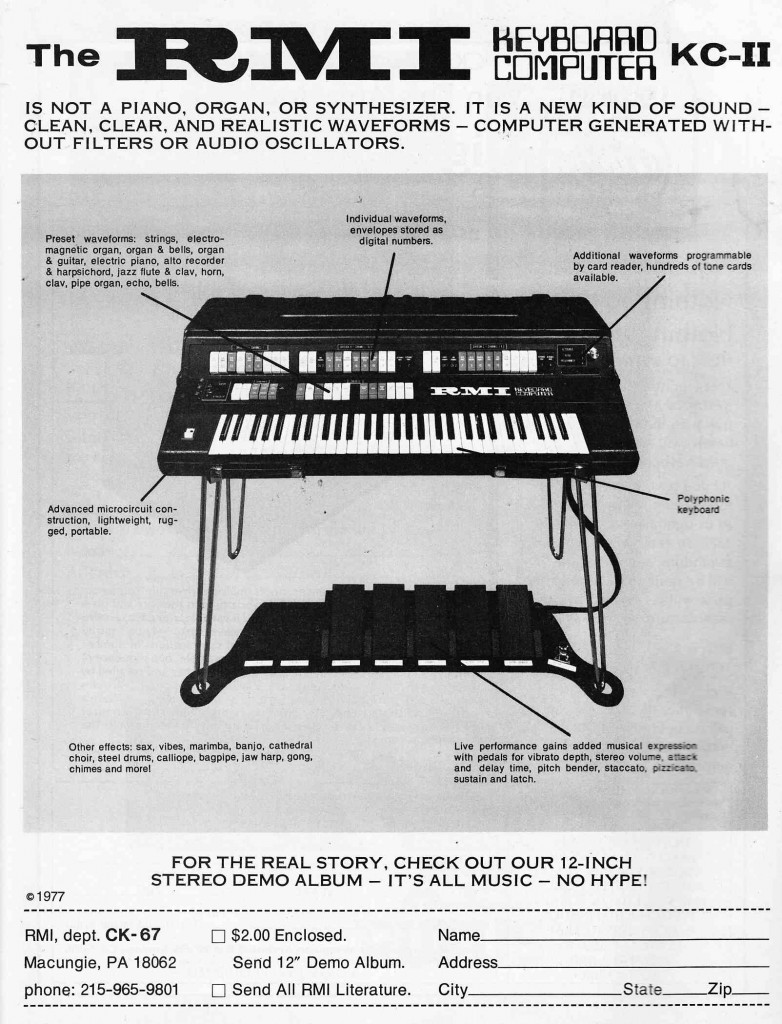 The RMI KC-II Keyboard Computer. From what I gather, this device is essentially a RAMpler; not too different in basic principle from the epic Synclavier in that the user could input waveforms which would then be manipulated. This thing apparently cost $4700 which means that… yeah… there ain’t too many out there.
The RMI KC-II Keyboard Computer. From what I gather, this device is essentially a RAMpler; not too different in basic principle from the epic Synclavier in that the user could input waveforms which would then be manipulated. This thing apparently cost $4700 which means that… yeah… there ain’t too many out there.
 Roland MP-700 electronic piano
Roland MP-700 electronic piano
 Sequential Circuits Model 700 programmer. I assume that this thing has a bunch of jackpoints that you would connect to various I/O points on yr modular synth… anyone use one of these?
Sequential Circuits Model 700 programmer. I assume that this thing has a bunch of jackpoints that you would connect to various I/O points on yr modular synth… anyone use one of these?
 The Steiner-Parker Synthacon. A rare Minimoog-esque unit. Apparently used on IN THE LIGHT.
The Steiner-Parker Synthacon. A rare Minimoog-esque unit. Apparently used on IN THE LIGHT.
 The Strider Systems DCS1. I can’t find any info on this piece. Anyone?
The Strider Systems DCS1. I can’t find any info on this piece. Anyone?
 Yamaha CP-30, yet another electronic piano
Yamaha CP-30, yet another electronic piano
 The Yamaha YC-45, the flagship model of their YC series. The YCs are unapologetic “Combo Organs,” which explains why they are still in use while the string synths and electronic pianos rest mainly in landfills. These are great-sounding, versatile organs; they also weigh a metric tonne so be forewarned.
The Yamaha YC-45, the flagship model of their YC series. The YCs are unapologetic “Combo Organs,” which explains why they are still in use while the string synths and electronic pianos rest mainly in landfills. These are great-sounding, versatile organs; they also weigh a metric tonne so be forewarned.
Want more? Check out this site; this man has dedicated his entire blog to territory that I only dare visit.
Tomorrow: some interesting keyboard amps and FX from the era.
























